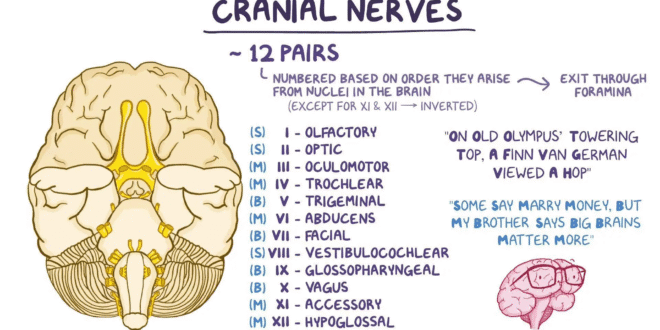
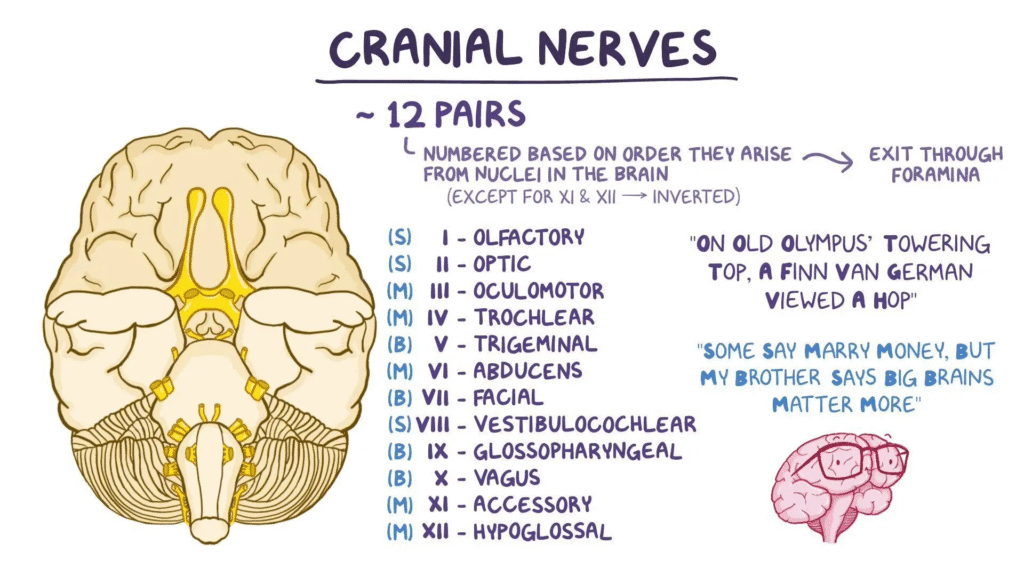
Cranial Nerves Details
HRTD Medical Institute. Mobile Number-01797522136.The nerves that are originated from the brain are cranial nerves. There are 12 pairs of cranial nerves in the human head. Your cranial nerves are a set of 12 nerves that send electrical signals between your brain and different parts of your head, face, neck and torso. These signals help you see, smell, taste, hear and move your facial muscles. Your cranial nerves begin toward the back of your brain. They’re a key part of your nervous system.
You might first think of your eyes, nose, ears and mouth when it comes to using your senses. But these body parts don’t work properly without healthy cranial nerves. You can also thank your cranial nerves for allowing you to make facial expressions and communicate.
How many cranial nerves are there?
You have 12 cranial nerve pairs. Each nerve pair splits to serve the two sides of your brain and body. For example, you have one pair of olfactory nerves. One olfactory nerve is on the left side of your brain, and one is on the right side of your brain.
Function
What is the function of the cranial nerves?
Your cranial nerves play a role in relaying sensory and/or movement (motor) information.
Sensory nerves can help you:
- Feel touch and sense pain and temperature.
- Hear.
- See.
- Smell.
- Taste.
Motor nerves play a role in controlling specific muscles. Some cranial nerves have both sensory and motor functions.
Your 12 cranial nerves each have a specific function. Healthcare providers categorize the cranial nerves based on number and function:
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII): Controlling tongue movement, which plays a role in speaking, eating and swallowing.
Olfactory nerve (CN I): Providing the sense of smell.
Optic nerve (CN II): Providing vision.
Oculomotor nerve (CN III): Opening and moving your eyes and adjusting pupil width.
Trochlear nerve (CN IV): Looking down and moving your eyes toward your nose or away from it.
Trigeminal nerve (CN V): Providing sensations in your eyes, most of your face and inside your mouth. It also allows you to chew food.
Abducens nerve (CN VI): Moving your eyes from left to right.
Facial nerve (CN VII): Controlling several facial muscles to make facial expressions and providing the sense of taste in part of your tongue.
Vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII): Providing the sense of hearing and balance.
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX): Providing taste sensations to part of your tongue and controlling muscles for swallowing. It also has parasympathetic nerve fibers that play a role in blood pressure regulation and saliva (spit) production.
Vagus nerve (CN X): Regulating several automatic bodily processes, including your digestion, blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, mood, saliva production and more. It’s the main nerve of your parasympathetic nervous system.
Accessory nerve or spinal accessory nerve (CN XI): Controlling shoulder and neck movement.
Which is the smallest cranial nerve?
The Trochlear nerve (Cranial Nerve IV) is the smallest cranial nerve, notable for its long intracranial course and the unique characteristic of emerging from the dorsal side of the brainstem. It primarily serves a motor function, controlling the superior oblique muscle to direct eye movement.
Key Characteristics of the Trochlear Nerve
- Smallest Cranial Nerve: It is considered the smallest by virtue of having the fewest axons compared to the other 11 cranial nerves.
- Longest Intracranial Course: Despite its small size, it has the longest path within the skull of all cranial nerves, making it susceptible to damage from increased intracranial pressure.
- Unique Origin: Unlike most other cranial nerves, it is the only one to emerge from the dorsal (back) aspect of the brainstem.
- Motor Function: It is a somatic efferent (motor) nerve, solely responsible for innervating the superior oblique muscle of the eye.
- Eye Movement: By controlling the superior oblique, it contributes to eye movement by enabling intorsion (inward rotation), depression (downward movement), and abduction (outward movement) of the eyeball.
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka