Heart Failure Details
HRTD Medical Institute. Mobile Number- 01987073965. Heart failure occurs when the heart muscle doesn’t pump blood as well as it should. When this happens, blood often backs up and fluid can build up in the lungs, causing shortness of breath.
Heart failure is a chronic condition where the heart muscle, weakened or stiffened, struggles to pump enough blood and oxygen to meet the body’s needs. This inability to keep up with the heart’s workload can lead to symptoms like shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid buildup (swelling) in the legs, ankles, and lungs. It is not that the heart has stopped, but rather it functions with reduced efficiency, requiring management through medication, lifestyle adjustments, and potentially medical devices.
হার্ট ফেইলিউর হলো একটি দীর্ঘস্থায়ী অবস্থা যেখানে হৃদপিণ্ডের পেশী দুর্বল বা শক্ত হয়ে যায় এবং শরীরের চাহিদা পূরণের জন্য পর্যাপ্ত রক্ত এবং অক্সিজেন পাম্প করতে ব্যর্থ হয়। হৃদপিণ্ডের কাজের চাপের সাথে তাল মিলিয়ে চলতে না পারার ফলে শ্বাসকষ্ট, ক্লান্তি এবং পা, গোড়ালি এবং ফুসফুসে তরল জমা (ফোলা) এর মতো লক্ষণ দেখা দিতে পারে। এর অর্থ এই নয় যে হৃদপিণ্ড বন্ধ হয়ে গেছে, বরং এটির কার্যকারিতা হ্রাস পেয়েছে, যার জন্য ওষুধ, জীবনযাত্রার সমন্বয় এবং সম্ভাব্য চিকিৎসা সরঞ্জামের মাধ্যমে ব্যবস্থাপনার প্রয়োজন হয়
What happens in heart failure?
- Reduced pumping ability: The heart muscle becomes too weak or too stiff to pump blood effectively throughout the body.
- Fluid buildup: As the heart struggles to pump, blood returning from the body can back up, leading to fluid accumulation (congestion) in various parts of the body, such as the lungs, legs, and feet.
- Lack of oxygen: The reduced blood flow means the body’s muscles and organs don’t receive the necessary oxygen, resulting in fatigue.
হৃদযন্ত্রের ব্যর্থতায় কী ঘটে?
- পাম্পিং ক্ষমতা হ্রাস: হৃদপিণ্ডের পেশীগুলি এত দুর্বল বা খুব শক্ত হয়ে যায় যে সারা শরীর জুড়ে কার্যকরভাবে রক্ত পাম্প করতে পারে না।
- তরল জমা: যখন হৃদপিণ্ড পাম্প করতে লড়াই করে, তখন শরীর থেকে ফিরে আসা রক্ত আবার জমা হতে পারে, যার ফলে শরীরের বিভিন্ন অংশে, যেমন ফুসফুস, পা এবং পায়ে তরল জমা (কনজেশন) হতে পারে।
- অক্সিজেনের অভাব: রক্ত প্রবাহ কমে যাওয়ার অর্থ হল শরীরের পেশী এবং অঙ্গগুলি প্রয়োজনীয় অক্সিজেন পায় না, যার ফলে ক্লান্তি দেখা দেয়।
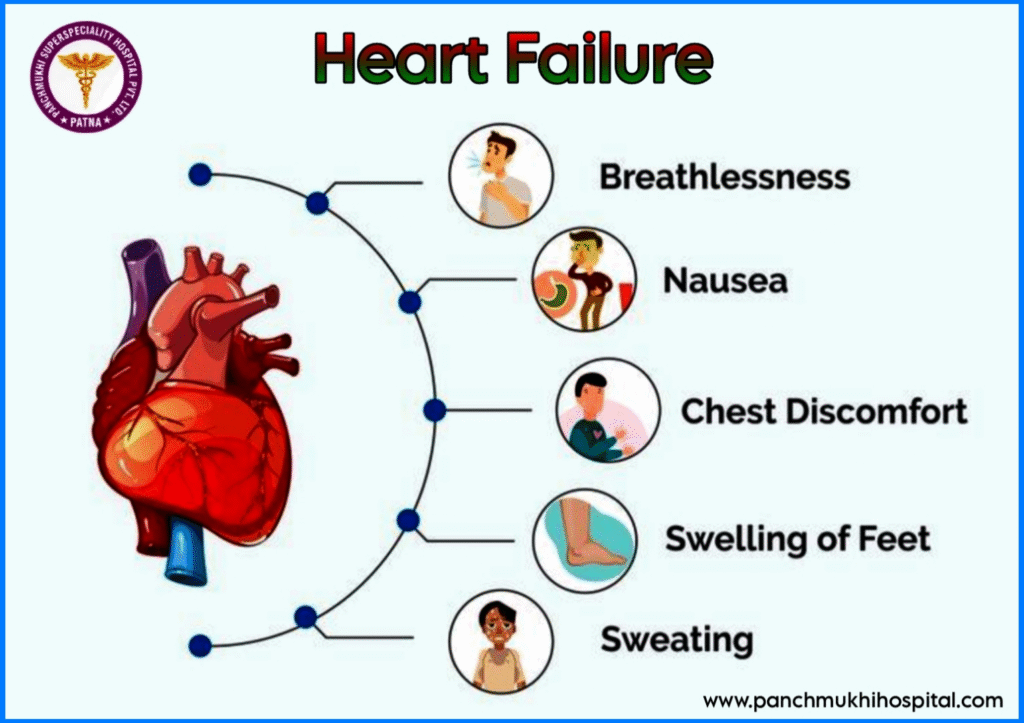
Common Symptoms of Heart Failure
- Shortness of breath, especially with activity or when lying down.
- Fatigue and lack of energy.
- Swelling (edema) in the legs, ankles, feet, and abdomen.
- Rapid weight gain due to fluid retention.
- A chronic cough or wheezing.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat.
হৃদযন্ত্রের ব্যর্থতার সাধারণ লক্ষণসমূহ
- শ্বাসকষ্ট, বিশেষ করে যখন কাজকর্ম করা হয় অথবা শুয়ে থাকা অবস্থায়।
- ক্লান্তি এবং শক্তির অভাব।
- পা, গোড়ালি, পা এবং পেটে ফোলাভাব (এডিমা)।
- তরল ধরে রাখার কারণে দ্রুত ওজন বৃদ্ধি।
- দীর্ঘস্থায়ী কাশি বা শ্বাসকষ্ট।
- দ্রুত বা অনিয়মিত হৃদস্পন্দন।
Causes of Heart Failure
Heart failure can result from various underlying heart conditions that damage or weaken the heart muscle over time, including: Coronary artery disease, High blood pressure (hypertension), Heart valve problems, Cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle), and Heart attack.
হৃদযন্ত্রের ব্যর্থতার কারণ
হৃদযন্ত্রের ব্যর্থতা বিভিন্ন অন্তর্নিহিত হৃদরোগের ফলে হতে পারে যা সময়ের সাথে সাথে হৃদযন্ত্রের পেশীকে ক্ষতিগ্রস্ত বা দুর্বল করে, যার মধ্যে রয়েছে: করোনারি ধমনী রোগ, উচ্চ রক্তচাপ (উচ্চ রক্তচাপ), হার্টের ভালভ সমস্যা, কার্ডিওমায়োপ্যাথি (হৃদযন্ত্রের পেশীর রোগ), এবং হার্ট অ্যাটাক।
Management
While heart failure is a lifelong condition, it can be managed with treatment to improve symptoms and quality of life:
- Medications: To help the heart pump better and reduce fluid.
- Lifestyle changes: Such as a healthy diet (low in salt), regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol.
- Devices: Pacemakers or other devices may be recommended in some cases.
- Cardiac rehabilitation: Programs designed to help patients regain energy and stamina.
ব্যবস্থাপনা
যদিও হৃদযন্ত্রের ব্যর্থতা আজীবনের জন্য স্থায়ী, তবুও লক্ষণ এবং জীবনের মান উন্নত করার জন্য চিকিৎসার মাধ্যমে এটি নিয়ন্ত্রণ করা যেতে পারে
ওষুধ: হৃদপিণ্ডকে ভালোভাবে পাম্প করতে এবং তরল পদার্থ কমাতে সাহায্য করার জন্য।
জীবনযাত্রার পরিবর্তন: যেমন একটি স্বাস্থ্যকর খাদ্য (লবণ কম), নিয়মিত ব্যায়াম, এবং ধূমপান এবং অতিরিক্ত অ্যালকোহল এড়িয়ে চলা।
যন্ত্র: কিছু ক্ষেত্রে পেসমেকার বা অন্যান্য ডিভাইস সুপারিশ করা যেতে পারে।
হৃদপিণ্ড পুনর্বাসন: রোগীদের শক্তি এবং সহনশীলতা ফিরে পেতে সাহায্য করার জন্য ডিজাইন করা প্রোগ্রাম।
What are the clinical features of right heart failure?
Right-sided heart failure symptoms include swelling (edema) in the ankles, legs, feet, and abdomen, unexplained weight gain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and issues like nausea, loss of appetite, and frequent urination. Fluid accumulation can also be seen as a distended neck vein. These symptoms result from the right side of the heart’s inability to effectively pump blood to the lungs, causing a backup of blood and fluid in the body.
Treatment of Heart Failure
Heart failure treatment focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression through a combination of lifestyle changes (like a healthy diet and exercise), medications (such as ACE inhibitors, diuretics, and beta-blockers), implanted devices (like pacemakers or Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators or ICDs), and potentially surgery or a heart transplant for severe cases.
Lifestyle Changes
- Diet: Adopt a healthy, balanced diet.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity as advised by your healthcare team.
- Weight Management: Maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the heart.
- Smoking Cessation: Stop smoking to prevent further damage to the heart.
Medications
- Diuretics: “Water pills” help reduce fluid build-up in the body.
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: These medications widen blood vessels, improving blood flow and reducing the heart’s workload.
- Beta-Blockers: Help protect the heart and improve its function.
- Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRAs): Also known as aldosterone antagonists, these help reduce fluid and improve heart function.
- Angiotensin Receptor-Neprilysin Inhibitors (ARNIs): A combination medication that helps reduce stress on the heart and improve its function.
- SGLT-2 Inhibitors: Medications that can reduce hospitalizations for heart failure, especially in patients with diabetes.
Devices
- Pacemakers: Help control your heart rhythm to reduce the heart’s workload.
- Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDs): Detect and treat dangerous, irregular heart rhythms to prevent sudden cardiac death.
- Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (CRT): A type of pacemaker that helps the heart beat more in sync, improving blood flow.
Surgery and Procedures
- Surgery: May be performed to improve blood flow to the heart, repair or replace a faulty valve, or address other underlying issues.
- Left Ventricular Assist Devices (LVADs): A mechanical pump for more advanced heart failure to assist a weakened heart.
- Heart Transplant: A surgical option for end-stage heart failure when other treatments are not successful.
Types of Heart Failure
Types of heart failure include
- Systolic heart failure
- Diastolic heart failure
- Acute heart failure
- Chronic heart failure
- Right side heart failure
- Left side heart failure
Investigation of Heart
Investigations for heart failure include a combination of initial tests like blood tests (especially BNP/NT-pro BNP), electrocardiogram (ECG), chest X-ray, and echocardiogram, which uses ultrasound to assess heart function. Further testing may involve exercise stress tests, cardiac catheterization, and advanced imaging like CT or MRI scans to evaluate the heart and coronary arteries in detail.
Initial assessments
- Blood tests: These can help diagnose underlying conditions and check for heart failure by measuring specific proteins (BNP/NT-pro BNP) that increase when heart pressures rise. Other blood tests look at kidney function, electrolytes, and thyroid function.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This quick and painless test records the heart’s electrical activity, helping to identify heart rate issues, prior heart attacks, or chamber enlargement.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can reveal an enlarged heart or fluid buildup in the lungs, which are signs of heart failure.
- Echocardiogram: Considered a crucial test, this ultrasound of the heart shows its structure, how well it is pumping, and the function of the valves. It also helps measure the ejection fraction, a key indicator of pumping efficiency.
Additional tests
- Exercise stress test: This test measures how the heart responds to physical activity, often by having you walk on a treadmill or ride a stationary bike while your heart is monitored.
- Cardiac catheterization: This procedure involves inserting a thin tube to directly measure pressures inside the heart chambers and to visualize the coronary arteries by injecting a dye.
- CT scan or MRI of the heart: These advanced imaging techniques provide detailed pictures of the heart’s structure and function, which can be used to evaluate coronary artery disease or other problems.
- Breathing tests: Tests like spirometry may be performed to assess for lung conditions that could be contributing to breathing problems.
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka