C Grade Pharmacy Course Details
HRTD Medical Institute. Mobile Number-01797522136 Hot line Number-01969947171.C Grade pharmacy course, also known as a C-Category or C-Grade Pharmacist course, is a short-term pharmacy training program in Bangladesh, typically lasting 3 months, 6 months. It is offered by various institutions and focuses on foundational pharmacy knowledge and skills. Upon completion, graduates can work as pharmacy assistants or salespersons.

Key Details C Grade Pharmacy Course
- Duration:3 months, 6months
- Focus:Foundational pharmacy knowledge, including human anatomy & physiology, pharmacology, first aid, and common drug information.
- Cost:Course fees can vary, but one example is 3months Tk 18,500, 6 months 30,500 tk including admission, monthly, and exam fees.
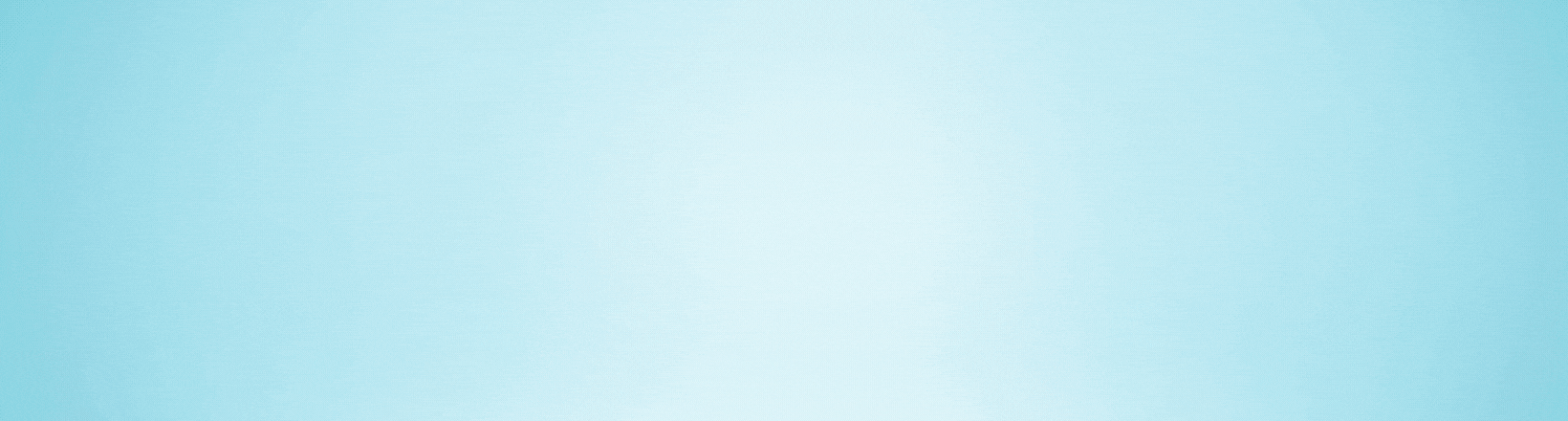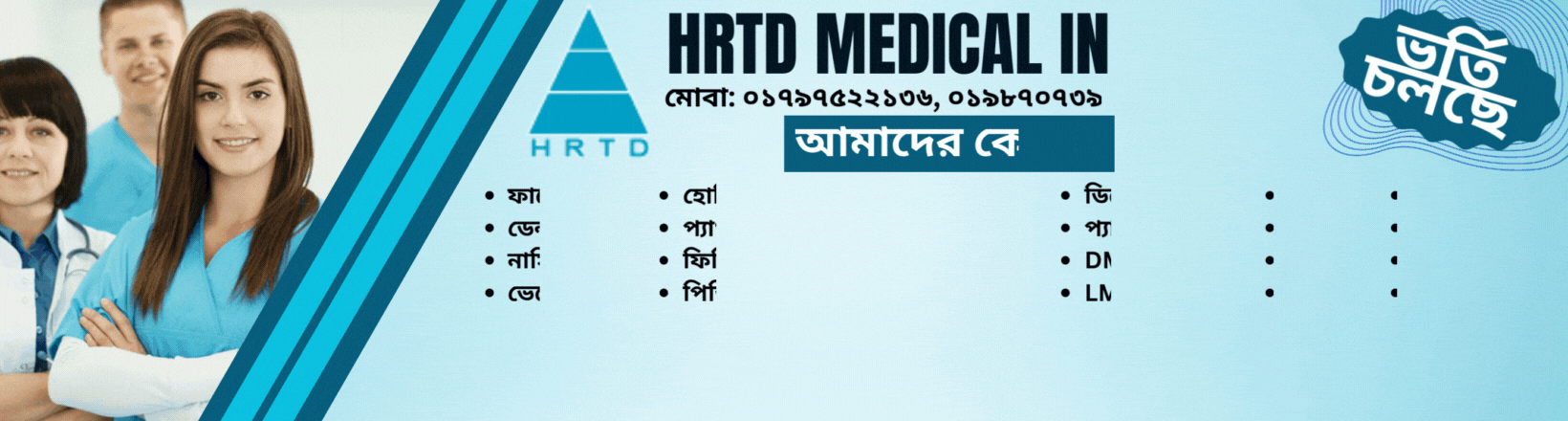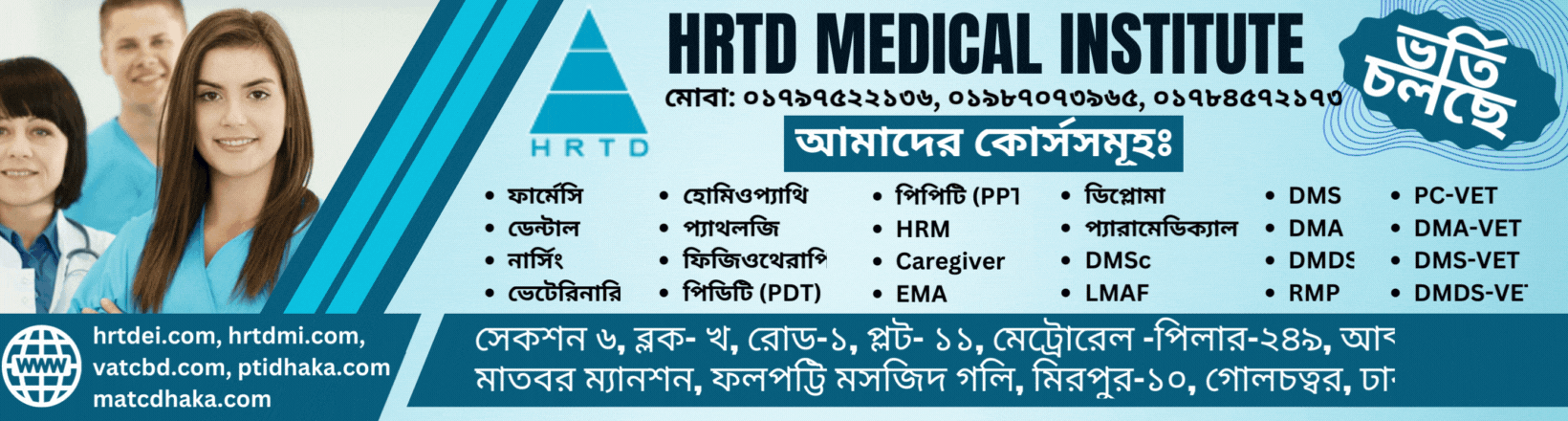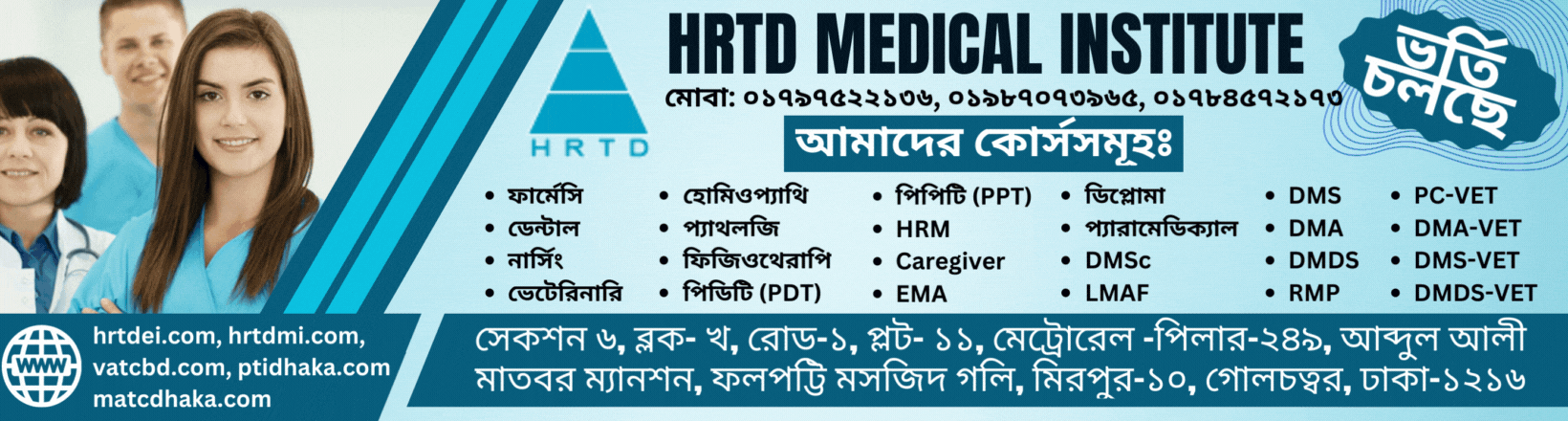
- Curriculum:Subjects typically include Human Anatomy & Physiology, Pharmacology-1, First Aid & Antimicrobial Drugs, Study of OTC Drugs, and Pharmacology-2.
- Career Opportunities:Graduates can work as pharmacists, pharmacy salesmen, or pharmacy assistants.
- Institutions:Various institutions in Dhaka, Bangladesh, offer the C Grade pharmacy course, including HRTD Medical Institute.
Example Course Details (from HRTD Medical Institute):
3 Months course details C Grade Pharmacy Course
- Course Fee: Tk 18,500.
- Admission Fee: Tk 10,500.
- Monthly Fee: Tk 2,000 x 3 months = Tk 6,000.
- Exam Fee: Tk 2,000.
- Subjects: 5 (as listed above).
- Class Schedule: Weekly 3 hours a day, Friday or Saturday or Monday.
6 Months course details C Grade Pharmacy Course
- Course Fee: TK 30,500
- Admission Fee: TK 10500
- Monthly Fee: TK 3000 x 6 months = TK 18000
- Exam Fee: TK 2000
- Subjects: 5 subjects
- Class Schedule: Weekly 3 hours a day Friday or Saturday or Monday
To find out more:
- Contact institutions like HRTD Medical Institute directly for the most up-to-date information.
- Search online for “C Grade pharmacy course Bangladesh” to explore different institutions and their offerings.
- Check the Pharmacy Council of Bangladesh (PCB) website for information about registration and course details
Location for C Grade Pharmacy Course
C Grade Pharmacy Course HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Folpotty Mosjid Goli (Bitul Mamur Jame Mosjid Goli), Plot No. 11, Metro Rail Piller No. 249, Mirpur 10 Golchattar, Dhaka.
Document for C Grade Pharmacy Course
C Grade Pharmacy Course for HRTD Medical Institute Photocopy of Certificate, Photocopy of NID, Passport Size Photo 4 Pcs. Without NID, a Birth Certificate is allowed for an emergency case.
Admission Eligibility for C Grade Pharmacy Course
C Grade Pharmacy Course Admission Eligibility. Mobile Number. 01987073965. 01941123488, 01797522136. SSC or Equivalent/HSC/ Degree/ Masters from any Background (Science/ Arts/ Commerce/ Technical).
Class System for C Grade Pharmacy Course
Class System for C Grade Pharmacy Course in Dhaka : Weekly Class 3 hours. For Job holders 3 hours in a day. The option days are Friday Morning Shift from 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, Friday Evening Shift from 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM, Monday Morning Shift from 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, Monday Evening Shift from 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM. Saturday Morning Shift from 10am to 1 Pm, Evening Shift from 3 pm to 6 pm.
For Regular Students Saturday 1 hour, Monday 1 hour, and Friday 1 hour. Morning Shift From 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, and Evening Shift From 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM.
Hostel Facilities in HRTD Medical Institute for C Grade Pharmacy Course
Hostal & Meal Facilities
The Institute has hostel facilities for the students. Students can take a bed in the hostel.
Hostel Fee Tk 3000/- Per Month
Meal Charges Tk 3000/- Per Month. ( Approximately )
হোস্টাল ও খাবার সুবিধা
ইনস্টিটিউটে শিক্ষার্থীদের জন্য হোস্টেল সুবিধা রয়েছে। ছাত্ররা হোস্টেলে বিছানা নিতে পারে।
হোস্টেল ফি 3000/- টাকা প্রতি মাসে,
খাবারের চার্জ 3000/- টাকা প্রতি মাসে।(প্রায়)
Address of HRTD Medical Institute for C Grade Pharmacy Course
আমাদের ঠিকানাঃ HRTD মেডিকেল ইন্সটিটিউট, আব্দুল আলী মাদবর ম্যানশন, সেকশন ৬, ব্লোক খ, রোড ১, প্লট ১১, মেট্রোরেল পিলার নাম্বার ২৪৯, ফলপট্টি মসজিদ গলি, মিরপুর ১০ গোলচত্ত্বর, ঢাকা ১২১৬ । মোবাইল ফোন নাম্বার ০১৭৯৭৫২২১৩৬, ০১৯৮৭০৭৩৯৬৫ ।
Our Address: HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Section-6, Block- Kha, Road- 1, Plot- 11, Metro Rail Pilar No. 249, Falpatty Mosjid Goli, Mirpur-10 Golchattar, Dhaka 1216. Mobile Phone No. 01797522136, 01987073965.
Teacher for C Grade Pharmacy Course
- Dr. Md. Sakulur Rahman, MBBS, CCD (BIRDEM), Course Director
- Dr. Sanjana Binte Ahmed, BDS, MPH, Assistant Course Director
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT Gyne, Assistant Course Director
- Dr. Suhana, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Dr. Danial Hoque, MBBS,
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS
- Dr. Afrin Jahan, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Dr. Ananna, MBBS
- Dr. Lamia Afroze, MBBS
- Dr. Amena Afroze Anu, MBBS, PGT Gyne, Assistant Course Director
- Dr. Farhana Antara, MBBS,
- Dr. Nazmun Nahar Juthi, BDS, PGT
- Dr. Farhana Sharna, MBBS
- Dr. Bushra, MBBS
- Dr. Turzo, MBBS
- Dr. Kamrunnahar Keya, BDS, PGT (Dhaka Dental College)
- Dr. Shamima, MBBS, PGT Gyne
- Dr. Alamin, MBBS
- Dr. Benzir Belal, MBBS
- Dr. Disha, MBBS
- Dr. Mahinul Islam, MBBS
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Dr. Anika, MBBS, PGT
- Dr. Jannatul Ferdous, MBBS, PGT Gyne
- Dr. Jannatul Aman, MBBS, PGT
- Dr. Rayhan, BPT
- Dr. Abu Hurayra, BPT
- Dr. Sharmin Ankhi, MBBS, PGT Medicine
- Md. Monir Hossain, B Pharm, M Pharm
- Md. Monirul Islam, B Pharm, M Pharm
- Md. Feroj Ahmed, BSc Pathology, PDT Medicine
Practical class for C Grade Pharmacy Course
- Heart Beat, Heart Rate
- Heart Sound, Pulse
- Blood Pressure, Hypertension, Hypotension
- First Aid Box
- Auscultation
- Inhaler, Rota haler
- Nebulizer
- Glucometer Blood Glucose
- Injection I/V
- Injection I/M
- Cleaning, Dressing, Bandaging
- Saline
- CPR
- Stitch
- Body Temperature
- Nasal Tube Gel, Hand Wash
- Blood Grouping
- Cyanosis, Dehydration Test, Edema Test
Heart Beat, Heart Rate for C Grade Pharmacy Course
Heart Beat for C Grade Pharmacy Course
Understanding the mechanics of the human heart through practical application is a foundational exercise in biology and medicine. The “heartbeat” is not just a sound; it is the physical manifestation of the cardiac cycle—the sequence of contraction (systole) and relaxation (diastole) that propels blood throughout the body. In a practical laboratory or home setting, measuring these beats allows us to observe how the body maintains homeostasis by adjusting blood flow in response to different stimuli, such as physical exertion, stress, or even temperature changes.
ব্যবহারিক প্রয়োগের মাধ্যমে মানুষের হৃদপিণ্ডের যান্ত্রিকতা বোঝা জীববিজ্ঞান এবং চিকিৎসাবিদ্যার একটি মৌলিক অনুশীলন। “হৃদস্পন্দন” কেবল একটি শব্দ নয়; এটি হৃদযন্ত্রের চক্রের শারীরিক প্রকাশ – সংকোচন (সিস্টোল) এবং শিথিলকরণ (ডায়াস্টোল) এর ক্রম যা সারা শরীরে রক্তকে চালিত করে। একটি ব্যবহারিক পরীক্ষাগারে বা বাড়িতে, এই স্পন্দনগুলি পরিমাপ করার মাধ্যমে আমরা পর্যবেক্ষণ করতে পারি যে শারীরিক পরিশ্রম, চাপ, এমনকি তাপমাত্রার পরিবর্তনের মতো বিভিন্ন উদ্দীপনার প্রতিক্রিয়ায় রক্ত প্রবাহকে সামঞ্জস্য করে শরীর কীভাবে হোমিওস্ট্যাসিস বজায় রাখে।
Subjects list of C Grade Pharmacy Course
1.Anatomy & Physiology =100
2.Pharmacology =100
3.First Aid & Antimicrobial Drugs =100
4.Study of OTC Drugs =100
5.Pharmacology-2 =100
Anatomy & Physiology C Grade Pharmacy Course
Anatomy and Physiology is an important subject for medical science. The study of Body Structure and its functions is Anatomy and Physiology. The systems of the Human Body are the Nervous System, Digestive System, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Endocrine System, Immune System, Lymphatic System, Covering System, and Urinary System
চিকিৎসা বিজ্ঞানের জন্য অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ বিষয়। শারীরিক গঠন এবং এর কার্যকারিতা অধ্যয়নের জন্য অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি। মানবদেহের সিস্টেমগুলি হল স্নায়ুতন্ত্র, পাচনতন্ত্র, শ্বাসযন্ত্র, হৃদযন্ত্র, কঙ্কালতন্ত্র, পেশীতন্ত্র, অন্তঃস্রাবী ব্যবস্থা, রোগ প্রতিরোধ ব্যবস্থা, লিম্ফ্যাটিক সিস্টেম, আবরণ ব্যবস্থা এবং মূত্রতন্ত্র।
Anatomy and physiology are the two primary biological sciences used to understand the human body. While anatomy focuses on structure, physiology focuses on function. Together, they describe what the body is and how it works to maintain life through a state of balance called homeostasis.
মানবদেহ বোঝার জন্য অ্যানাটমি এবং ফিজিওলজি হল দুটি প্রাথমিক জৈবিক বিজ্ঞান। অ্যানাটমি গঠনের উপর দৃষ্টি নিবদ্ধ করে, তবে ফিজিওলজি ফাংশনের উপর দৃষ্টি নিবদ্ধ করে। একসাথে, তারা বর্ণনা করে যে শরীর কী এবং এটি হোমিওস্ট্যাসিস নামক ভারসাম্যের অবস্থার মাধ্যমে জীবন বজায় রাখার জন্য কীভাবে কাজ করে।

Core Definitions
- Anatomy: The study of internal and external body structures and their physical relationships. It is often divided into:
- Gross (Macroscopic) Anatomy: Study of structures visible to the naked eye, such as organs and bones.
- Microscopic Anatomy: Study of structures requiring magnification, including cytology (cells) and histology (tissues).
- Physiology: The study of how these structures function and work together to support life. Sub-branches include pathophysiology (study of disordered function during disease) and cellular physiology.
Levels of Biological Organization
The body is organized from the simplest to the most complex building blocks:
- Chemical Level: Atoms and molecules (e.g., DNA, glucose).
- Cellular Level: The basic functional units of life.
- Tissue Level: Groups of similar cells performing a common function.
- Organ Level: Different tissues working together (e.g., the heart or stomach).
- Organ System Level: Groups of organs coordinating for a major purpose (e.g., the digestive system).
- Organism Level: The whole human being.
Major Body Systems
The human body consists of 11 primary organ systems:
- Skeletal & Muscular: Provide structure, support, and movement.
- Nervous & Endocrine: Coordinate and regulate bodily responses and communication.
- Cardiovascular & Respiratory: Deliver oxygen and nutrients while removing waste like carbon dioxide.
- Digestive & Urinary: Process nutrients and eliminate waste to maintain fluid balance.
- Integumentary: The skin, hair, and nails that protect the body.
- Lymphatic/Immune: Defend against pathogens.
- Reproductive: Facilitate the production of offspring
Pharmacology C Grade Pharmacy Course
Drugs are chemicals that can react with cells, tissues, and organs of the body. Here we discuss group-wise drugs and their medicines. Common Groups of Drugs are Pain Killer Drugs, Anti Ulcer Drugs, Anti Vomiting Drugs, Anti Viral Drugs, Laxative Drugs, Motility Drugs and Antimotility Drugs, Bronchodilator Drugs, Antibiotic Drugs, Anti Fungal Drugs, Anti Thrombotic Drugs, Anti Protozoal Drugs, Anthelmintic Drugs, Anti Hypertensive Drugs, Beta Blocker Drugs, Calcium Channel Blocker Drugs, ACE Inhibitor Drugs, Hemostatic Drugs, Analgesic Drugs, Antipyretic Drugs, Steroid Drugs, NSAID Drugs, CNS Drugs, Neuropathic Pain Keller Drugs, Spasmodic Drugs, etc.
ওষুধ হলো এমন রাসায়নিক পদার্থ যা শরীরের কোষ, টিস্যু এবং অঙ্গগুলির সাথে বিক্রিয়া করতে পারে। এখানে আমরা গ্রুপ-ভিত্তিক ওষুধ এবং তাদের ওষুধ নিয়ে আলোচনা করব। ওষুধের সাধারণ গ্রুপগুলি হল ব্যথানাশক ওষুধ, আলসার-বিরোধী ওষুধ, বমি-বিরোধী ওষুধ, ভাইরাস-বিরোধী ওষুধ, ল্যাক্সেটিভ ওষুধ, গতিশীলতা ওষুধ এবং অ্যান্টিমোটিলিটি ওষুধ, ব্রঙ্কোডাইলেটর ওষুধ, অ্যান্টিবায়োটিক ওষুধ, ছত্রাক-বিরোধী ওষুধ, থ্রম্বোটিক ওষুধ, প্রোটোজোয়াল ওষুধ, অ্যান্থেলমিন্টিক ওষুধ, হাইপারটেনসিভ ওষুধ, বিটা ব্লকার ওষুধ, ক্যালসিয়াম চ্যানেল ব্লকার ওষুধ, এসিই ইনহিবিটর ওষুধ, হেমোস্ট্যাটিক ওষুধ, অ্যানালজেসিক ওষুধ, অ্যান্টিপাইরেটিক ওষুধ, স্টেরয়েড ওষুধ, এনএসএআইডি ওষুধ, সিএনএস ওষুধ, নিউরোপ্যাথিক পেইন কেলার ওষুধ, স্প্যাসমডিক ওষুধ ইত্যাদি।
Pharmacology is the scientific study of how drugs and chemicals interact with living organisms to produce biological effects. It acts as a bridge science, integrating principles from biology, chemistry, and medicine to understand drug origins, properties, and mechanisms.
Core Branches
Pharmacology is primarily divided into two main areas that describe the relationship between a drug and the body:
- Pharmacokinetics: What the body does to the drug. This is often summarized by the acronym ADME:
- Absorption: How the drug enters the bloodstream.
- Distribution: How the drug travels through the body to various tissues.
- Metabolism: How the body breaks down the drug, primarily in the liver.
- Excretion: How the body eliminates the drug, usually via the kidneys or bile.
- Pharmacodynamics: What the drug does to the body. It focuses on the molecular, biochemical, and physiological effects of drugs, including their mechanisms of action at receptor sites.
Key Sub-disciplines
- Clinical Pharmacology: The application of pharmacological methods in humans to ensure safe and effective medication use.
- Toxicology: The study of the adverse effects of chemicals and the assessment of risks associated with poisons.
- Pharmacogenomics: Investigates how an individual’s genetic makeup affects their response to drugs, paving the way for personalized medicine.
- Neuropharmacology: Focuses on drugs that affect the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Pharmacology vs. Pharmacy
While often confused, these fields have distinct focuses:
- Pharmacology is a research-oriented science centered on drug discovery, mechanisms, and laboratory-based investigation.
- Pharmacy is a clinical healthcare profession focused on the preparation, dispensing, and safe administration of medicines directly to patients.
Modern Applications
As of 2026, pharmacology continues to evolve through:
- Drug Discovery: Identifying new targets for treatment, such as G protein-coupled receptors or enzymes.
- Regulatory Oversight: Bodies like the FDA (USA) and EMA (EU) use pharmacological data to approve new medications.
- Advanced Research: Utilizing AI and network pharmacology to predict drug-drug interactions and optimize therapeutic strategies.
First Aid & Antimicrobial Drugs for C Grade Pharmacy Course
First Aid 1&2 for C Grade Pharmacy Course
First Aid 1 & 2 are sequential training levels, with Level 1 (Basic) covering essential life-saving skills like CPR, choking, bleeding, and shock for everyday emergencies, while Level 2 (Intermediate) builds on this with more advanced techniques like splinting, bandaging, managing specific conditions (heart attack, stroke), and handling complex injuries, preparing for higher-risk situations and broader workplace needs. Level 1 is fundamental for everyone, while Level 2 adds depth for comprehensive emergency response.
First Aid Level 1 (Basic)
- Focus: Foundational, essential skills for common emergencies.
- Skills: Scene assessment, CPR, choking, bleeding/wounds, burns, fainting, basic shock management.
- Best For: Low-risk settings like offices, schools, general staff.
First Aid Level 2 (Intermediate)
- Focus: Advanced, more detailed care beyond basic first aid.
- Skills: All Level 1 skills plus splinting, advanced bandaging, managing specific medical emergencies (heart attack, stroke, seizure), multiple injuries, drowning, electrocution.
- Best For: Higher-risk workplaces where more comprehensive care is needed before professional help arrives.
Key Differences & Progression
- Progression: Level 2 expands significantly on Level 1, providing more detailed knowledge and practical application.
- Scope: Level 1 teaches you what to do; Level 2 teaches you how to do it better and handle more complex scenarios.
Antimicrobial Drugs for C Grade Pharmacy Course
The subject of Antimicrobial Drugs covers medicines like antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitics, used to kill or inhibit microbes (bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites) causing infections in humans, animals, and plants, focusing on their mechanisms, selective toxicity, clinical use, and the critical threat of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) due to misuse, which renders them ineffective. It’s a vast field in pharmacology and microbiology, involving drug development, resistance monitoring, and stewardship.
Key Areas in Antimicrobial Drugs:
- Types of Agents: Antibiotics (bacteria), Antivirals (viruses), Antifungals (fungi), Antiparasitics (parasites).
- Mechanisms of Action (MOA): How they kill (bactericidal) or stop growth (bacteriostatic) by targeting unique microbial processes (e.g., cell wall synthesis).
- Selective Toxicity: Designing drugs to harm microbes without harming host cells, a core principle.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): Pathogens evolving to resist drugs, a major global health threat making infections hard to treat.
- Drug Classes: Examples include Penicillins, Tetracyclines, Macrolides, targeting different microbes or acting differently.
- Clinical Applications: Treating infections, prophylaxis (prevention), and impact on surgeries/chemotherapy.
Why it’s Important:
Antimicrobials are vital for modern medicine, but AMR threatens routine procedures like surgery and cancer treatment, making this subject crucial for public health and new drug discovery.
Study of OTC Drugs for C Grade Pharmacy Course
Studying Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs involves understanding their prevalence, usage patterns (like analgesics for headaches during exams), common types (antacids, cough suppressants), influencing factors (accessibility, advertising, education), risks (misuse, overdose, addiction), and the importance of self-care knowledge, safety (expiry dates, side effects), and regulation, often using surveys to assess public knowledge and practices. Key areas focus on pharmacology, public health, and patient behavior, highlighting self-medication trends and potential misuse.
Key Areas of Study for C Grade Pharmacy Course
- Usage Patterns & Prevalence: How often people use OTCs, common reasons (headaches, colds, fever), and demographics (age, gender, education).
- Common OTC Categories: Analgesics (pain relievers), antipyretics (fever reducers), antacids, cough/cold meds, antibiotics (often misused).
- Influencing Factors: Accessibility (pharmacies, stores), advertising, peer advice, perceived need for quick relief (exams).
- Risks & Misuse: Dangers of improper dosing (especially DXM, loperamide), addiction potential, side effects, interactions with prescribed drugs, and discarding expired meds.
- Knowledge & Practices: Public awareness of safe usage, expiry dates, potential side effects, and when to seek professional help (e.g., pregnant women).
- Regulation & Policy: Need for control, public education, and ensuring affordable healthcare alternatives.
Common Study Methods
- Surveys & Questionnaires: Structured tools used to gather data on demographics, knowledge, attitudes, and practices from populations (like university students).
- Cross-Sectional Studies: Design to describe current self-medication patterns.
- Data Analysis: Statistical methods (like logistic regression) to find correlations between demographics and OTC use.
Why It Matters (Especially in Dhaka/Similar Regions)
- High prevalence of self-medication due to easy access.
- Misuse of antibiotics and NSAIDs signals a need for better control and education.
- Understanding these trends helps develop strategies to improve public health and responsible drug use
Pharmacology-2 for C Grade Pharmacy Course
Pharmacology-2 subjects typically cover drugs acting on specific body systems, moving beyond general principles (like pharmacokinetics/dynamics) into detailed therapeutics for cardiovascular, central nervous system (CNS), respiratory, gastrointestinal (GIT), and endocrine systems, plus antimicrobials, antivirals, and toxicology, focusing on mechanisms, uses, side effects, and practical applications like prescription writing for various conditions.
Here are the common subject areas in Pharmacology-2:
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Cholinergics, anticholinergics, adrenergics, blockers, muscle relaxants.
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Sedatives, hypnotics, anxiolytics, antipsychotics, antidepressants, anti-epileptics, Parkinson’s drugs, opioids, local anesthetics.
- Cardiovascular System: Antihypertensives, antianginals, antiarrhythmics, diuretics, drugs for heart failure, lipids, thrombosis.
- Respiratory System: Antihistamines, cough suppressants, expectorants.
- Gastrointestinal System: Antacids, laxatives, antiemetics, anti-ulcers, drugs for liver/pancreas.
- Anti-infectives: Antibacterial (penicillins, quinolones), antifungal, antiviral, antitubercular, antimalarial, anthelmintic drugs.
- Endocrine System: Corticosteroids, antidiabetics, thyroid drugs.
- Blood & Lymphatics: Anticoagulants, thrombolytics, haemopoietics.
- Chemotherapy: Anticancer (antineoplastics).
- Toxicology: Basic principles, poisoning, toxicity testing.
- Practical Skills: Prescription writing, bioassays, clinical application
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka