Digestion & Metabolism Details
Digestion & Metabolism. Mobile Phone Number 01797522136, 01987073965. The process of extracting food ingredients from food is called Digestion. Making food ingredients suitable for absorption is called Digestion. Eg: Meat is a protein food. That is, there is the protein inside the meat. Digestion is the process of extracting protein from meat.
Metabolism is the process of making food materials useful for use by the cells. By using food materials, cells produce energy and perform all other functions. It means that first digestion of food occurs, and then metabolism occurs. Digestion and Metabolism are important subjects for Gastrology, Hepatology, and Endocrinology. We discuss digestion and metabolism broadly in the DMS Course, DMA Course, PDT Gastrology, PDT Hepatology, PDT Diabetology, and PDT Endocrinology Courses. All these courses are available at HRTD Medical Institute.
1.Define digestion.
খাদ্য থেকে খাদ্যের উপাদান গুলি বের করার প্রক্রিয়াকে Digestion বা পরিপাক বা হজম বলে।অথবা খাদ্যের উপাদান গুলি শোষনের উপযুক্ত করাকে Digestion বা পরিপাক বা হজম বলে। যেমন: মাংস একটি protein জাতীয় খাদ্য। অর্থাৎ মাংসের ভেতরে থাকে protein. মাংস থেকে protein বের করার প্রক্রিয়া হচ্ছে Digestion বা পরিপাক বা হজম।
2.Define Metabolism
খাদ্যের উপাদান গুলিকে কোষ দ্বারা ব্যবহারের উপযোগী করার প্রক্রিয়াকে Metabolism বা বিপাক বলে।খাদ্যের উপাদান গুলিকে ব্যবহার করেই কোষসমূহ শক্তি উৎপাদন করে এবং অন্যান্য যাবতীয় কাযসম্পাদন করে। অর্থৎ প্রথমে ঘটে খাদ্যের পরিপাক, তারপর ঘটে বিপাক।
3.Metabolism এর আধুনিক সংজ্ঞা দাও।
খাদ্যের উপাদান গুলি থেকে শক্তি উৎপাদন প্রক্রিয়াকে Metabolism বা বিপাক বলে। শক্তি উৎপাদিত হয় কোষের ভিতরের Mitochondria তে।
জীবদেহে সংঘটিত পর্যায় ক্রমিক জৈব রাসায়নিক বিক্রিয়াকে Metabolism বা বিপাক বলে। ইহা Enzyme, Co- enzyme প্রভৃতি অনুঘটকের উপস্থিতিতে সংঘটিত হয় এবং Hormone ও Vitamin দ্বারা নিয়ন্ত্রিত হয়।
4. Metabolism কে শ্রেণী বিন্যাস কর, সংজ্ঞা দাও এবং উদাহরন দাও।
Metabolism দুই প্রকার
- Anabolism
- Catabolism
Anabolism: সরল বস্তু জটিল বস্তুতে রুপান্তরিত হওয়াকে Anabolism বলে। যেমন Glucose লিভার এ সশ্চিত হয় Glycogen হিসেবে।
Catabolism: জটিল বস্তু সরল বস্তুতে রুপান্তরিত হওয়াকে Catabolism বলে। যেমন Liver এর সশ্চিত Glycogen ভেঙ্গে Glucose এ পরিনত হয়।
5. কিছু Anabolism এবং কিছু Catabolism বিক্রিয়া উল্লেখ কর।
Anabolism (উপচিতি) বিক্রিয়াঃ সংশ্লেষণ ও শক্তি সন্চয়ন মূলক বিক্রিয়া যেখানে সরল বস্তু সমূহ জটিল গাঠনিক বস্তুতে পরিনত হয়।
- ফ্লকোজ থেকে গ্লাইকোজেনে রুপান্তর (Glycogenesis)
- লিপিড সংশ্লেষণ (Lipogenesis)
- Protein সংশ্লেষণ (Protein synthesis)
- কিটোন বডি সংশ্লেষণ
- ইউরিয়া সংশ্লেষণ
- কোলেস্টেরল সংশ্লেষণ
Catabolism (অবচিতি) বিক্রিয়াঃ শক্তি সরবরাহের লক্ষে যে সকল বিক্রিয়ার মাধ্যমে জটিল পদার্থ সমূহ সরল পদার্থে রুপান্তরিত হয়।
- Glycogen ভেঙ্গে Glucose এ রূপান্তর।
- Glucose ভেঙ্গে যাওয়া (Glycolysis)
- Lipid ভেঙ্গে যাওয়া (Lipolysis)
- Protein ভেঙ্গে যাওয়া (Proteolysis/ Protein catabolism)
6. Mention the digestion of protein.
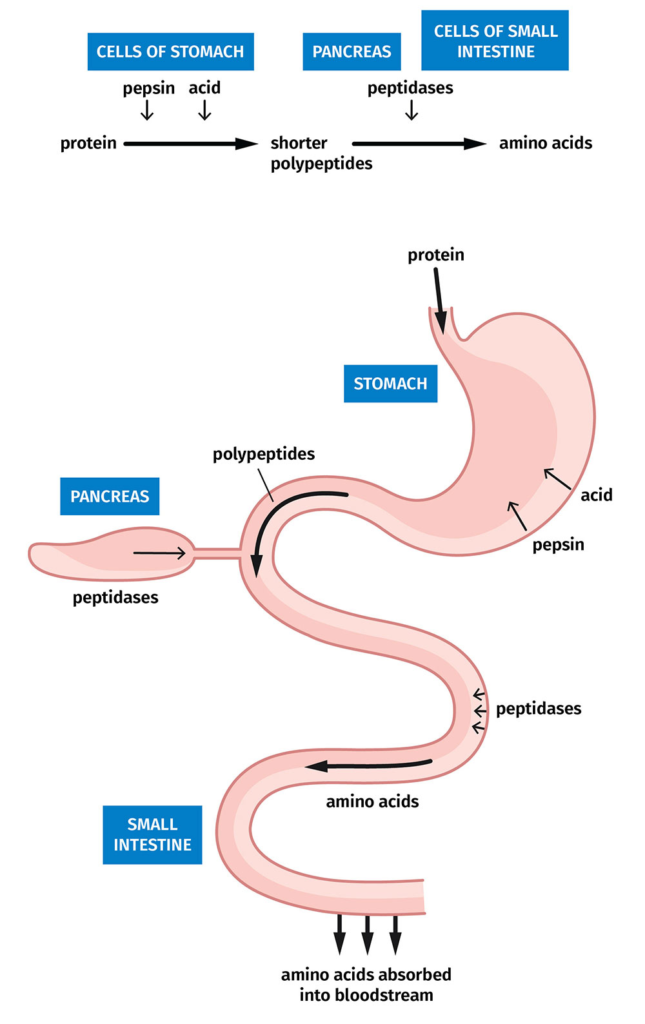
Fig: Digestion of protein
7. Mention the protein metabolism in the human body.
- tissue protein
- Urea
- Plasma Protein
- Stored
- Fibrinogen
- Ammo acid
- Amino
- Protein Synthes acid”
- Glycogen
- Urea
- Ileum
- Amino acid
- Urine Urea
8. Mention the carbohydrate digestion in the human body.
(1) In Oral Cavity: Saliva তে থাকে টায়ালিন নামক Enzyme. ইহা carbohydrate জাতীয় খাবারকে Maltose এ পরিনত করে।
Carbohydrate food
- Maltose
(2) In Duodenum: Pancreatic Juice এ থাকে Amylase নামক Enzyme. ইহা Maltose কে Glucose এ পরিনত কবে। Maltose Glucose
(3) In Intestine (Duodenum, Jejunum & Ilium): Intestine 3 Maltase, Lactase & Sucrase নামক Enzyme নিঃসৃত হয়।
- Maltose
- Glucose
- Lactose
- Glucose + Galactose
- Sucrose
- Glucose + Fructose
Intestine দ্বারা সহজেই Glucose, Fructose এবং Galactose শোষিত হয়।
9. Define Enterocrinin. Mention the secretion and function of Enterocrinin.
Enterocrinin: Enterocrinin is an enteric hormone. It is secreted from the ilium of the small intestine.
Functions of enterocrinin
It stimulates the secretion of
- Sucrase
- Lactase
- Invertase
- Maltase
- The above 4 enzymes secrete from the ilium
10. Mention the different types of polysaccharides.
There are three common and principal types of polysaccharides.
- Cellulose (Wood)
- Starch (Rich, bread, potatoes, and barley)
- Glycogen
All these polysaccharides are made by glucose molecules joining together in different ways.
Some animals can digest cellulose with the help of symbiotic microorganisms that live in their guts.
11. Mention the chemical formula of cellulose, starch, glycogen, sugar, sucrose, maltose, glucose, fructose, and galactose.
- cellulose (C6H10O5)n
- starch (C6H10O5)n
- glycogen (C6H10O5)n
- sugar C12H22O11
- sucrose C12H22O11
- maltose C12H22O11
- glucose C6H12O6
- fructose C6H12O6
- galactose C6H12O6
বিঃ দ্রঃ Monosaccharide থেকে Disaccharide তৈরী করতে H2O তৈরী হয়। অথবা Disaccharide থেকে polysaccharides তৈরী করতে ও H2O তৈরী হয়।
12. Mention the carbohydrate metabolism in the human body.
Carbohydrate metabolism in the human body.
13. Define fat with examples.
Fat হচ্ছে এক ধরনের তৈলাক্ত পদার্থ যা প্রাণী দেহে skin এর নিচে এবং কোন কোন organ এর উপরে সন্চিত হয়।
Fat consists of three acids and a glycerol, also called triacyglycerols or triglycerides.
Dehydration reaction এর মাধ্যমে তিনটি fatty acid এবং glycerol যুক্ত হয়ে fat তৈরী করে। এই বিক্রিয়ায় তিন অনু পানি যুক্ত হয়।
14. Glycerol এবং Triglycerides কি?
Glycerol: Glycerol is a kind of alcohol.
Triglycerides: Triglycerides হচ্ছে esters যেখানে এক বা একাধিক ধরনের তিনটি fatty acid এর অনু এবং Glycerol নামক এসকোহল থাকে।
15. Mention the Fat digestion in the human body.
Duodenum এর ক্ষারীয় মাধ্যমে pancreatic lipase enzyme দ্বারা Fat digestion সম্পন্ন হয়।
Fat + Fatty acids Glycerol
যেমন-
- Triglycerides Monoglycerides + Diglycerides
- Fatty acid +Fatty acids
- Glycerol +Glycerol
Next, the glycerol and fatty acid will move to the small intestine so that they can be absorbed into blood circulation. Griffin (2009) explains that the glycerol and fatty acid will pack together to form a chylomicron, whose role will be to transport the triglycerides to the liver
16. Mention the names of common fatty acids in human physiology.
- Formic acid
- Acetic acid
- Propionic acid
- Butyric acid
- Capric acid
- Palmitic acid
- Palmitoleic acid
- Stearic acid
- Oleic acid
- Linoleic acid
- Linolenic acid
- Arachidonic acid
- Lignoceric acid
- Nervonic acid
17. Define Chylomicron.
Chylomicron: A small fat globule composed of protein and lipid (fat). Chylomicrons are found in the blood and lymphatic fluid where they serve to transport fat from its port of entry in the intestine to the liver and to adipose (fat) tissue. After a fatty meal, the blood is so full of chylomicrons that it looks milky.
18. Mention the fatty acid metabolism in the human body.
Fatty acid metabolism consists of catabolic processes that generate energy, and anabolic processes that create biologically important molecules (triglycerides. phospholipids, second messengers, local hormones, and ketone bodies). Fatty acids are a family of molecules classified within the lipid macronutrient class
19. Mention the reaction by which Triglycerides are formed.
In triglycerides, the hydroxyl groups of the glycerol join the carboxyl groups of the fatty acid to form ester bonds
HOCH2CH (OH) CH2OH + RCO₂H + R’CO₂H + R”CO₂H→ RCO₂CH₂CH (O₂CR’) CH₂CO₂R” + 3H2O
20. Mention the metabolic end products of food.
Metabolic end products of foods are:
- Energy
- CO2
- H2O
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Creatinine
21. Mention separately the metabolic end products of foods.
Metabolic end products of protein: Energy, Urea, Uric acid, Creatinine.
Metabolic end products of fat: Energy, CO2, H2O
Metabolic end products of carbohydrate: Energy, CO2, H2O
22. Which vitamins are required in glucose metabolism?
- Thiamin
- Niacin
- Pantothenic acid
CHROMIUM is involved in carbohydrate, lipid (fats), and nucleic acid metabolism. It functions in carbohydrate and lipid (fat) metabolism as a potentiator of insulin action.
NIACIN is a B-complex nutrient that aids in the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.. VITAMIN B-1 is needed for carbohydrate metabolism.
23. Mention the sources of thiamine.
Sources of thiamine: Food sources of thiamine include beef, liver, dried milk, nuts, oats, oranges, pork, eggs, seeds, legumes, peas, and yeast. Foods are also fortified with thiamine. Some foods that are often fortified with B1 are rice, pasta, breads, cereals, and flour.
24. Mention the sources of niacin.
Many foods are rich in niacin, especially animal products like meat, fish, and poultry Vegetarian sources include avocado, peanuts, whole grains, mushrooms, green peas, and potatoes.
25. Mention the sources of pantothenic acid.
Sources of pantothenic acid: Animal liver and kidney, fish, shellfish, pork, chicken, egg yolk, milk, yogurt, legumes, mushrooms, avocados, broccoli, and sweet potatoes are good sources of pantothenic acid. Whole grains are also good sources of pantothenic acid, but processing and refining grains may result in a 35 to 75% loss.
26. What is FFA and ATGL?
FFA: Free Fatty Acid.
ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) is a triacylglycerol hydrolase that promotes the catabolism of stored fat
27. What is VLDL?
VLDL: Very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), density relative to extracellular water, is a type of lipoprotein made by the liver VLDL is assembled in the liver from triglycerides, cholesterol, and apolipoproteins. VLDL is converted in the bloodstream to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL).
28. Mention the functions of insulin.
Functions of insulin.
- Carbohydrate metabolism (
- Insulin decreases blood glucose by
- Glycogenesis
- Glycolysis
- Glucose uptake by cells
- Fatty acid synthesis
- Glycogenolysis
- Gluconeogenesis
- Lipolysis
- Insulin decreases blood glucose by
- Fat metabolism: Insulin exerts an anabolic (synthetic) role in fat metabolism. It causes-
- Lipogenesis
- Glycerol synthesis
- Triglyceride deposition
- Lipolysis by inhibition of hormone-sensitive lipase
- Ketogenesis
- Protein metabolism: Insulin exerts an anabolic (synthetic) role in protein metabolism. It causes-
- Amino acid uptake by cells
- Protein synthesis
- Protein breakdown
29. State the insulin lack in our body.
Effect of insulin deficiency
- Diabetes- because of the inability to use glucose, blood glucose level rises above normal.
- Insulin deficiency causes fat utilization for energy and finally causes acidosis.
- Insulin deficiency causes-
- Polyuria (Increased formation of urine)
- Polydipsia (Increased thrust)
- Polyphagia (Increased appetite)
- Asthenia (Weakness)
30. Mention the hormones that counteract the actions of insulin.
Or. Mention the hormones that have diabetogenic action.
Diabetogenic hormones are:
- Glucagon
- Catecholamine (Adrenaline & Nor-adrenaline)
- Cortisol
- GH
- Thyroid hormone
- TSH
- ACTH
31. What cells do not require insulin for glucose uptake?
Insulin-insensitive organs/cells are:
- Neurons
- Hepatocytes
- RBC, WBC
- Cornea
- Eye lens
- Epithelial cells or intestine and renal tubule
- Epithelial cells of choroid plexus.
32. What are the complications of diabetes mellitus?
Complications of diabetes mellitus:
- Microvascular complications:
- Diabetes retinopathy-Leading to blindness
- Diabetes nephropathy -leading to renal failure
- Diabetic neuropathy – Leading to sensory loss
- Autonomic neuropathy- Postural hypotension
- Foot disease – Ulceration.
- Macro-vascular complications:
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke
- Ischemia to peripheral circulation.
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka