Osteoarthritis Management details
Osteoarthritis Management. HRTD Medical Institute Hotline Number- 01969947171. Osteoarthritis Management should be based on a combination of non drug & drug treatments targeted for prevention, modifying risk & disease progression. Many courses of PDT Courses, DMA course, DMS course, DMDS course, Paramedical course of HRTD Medical Institute .
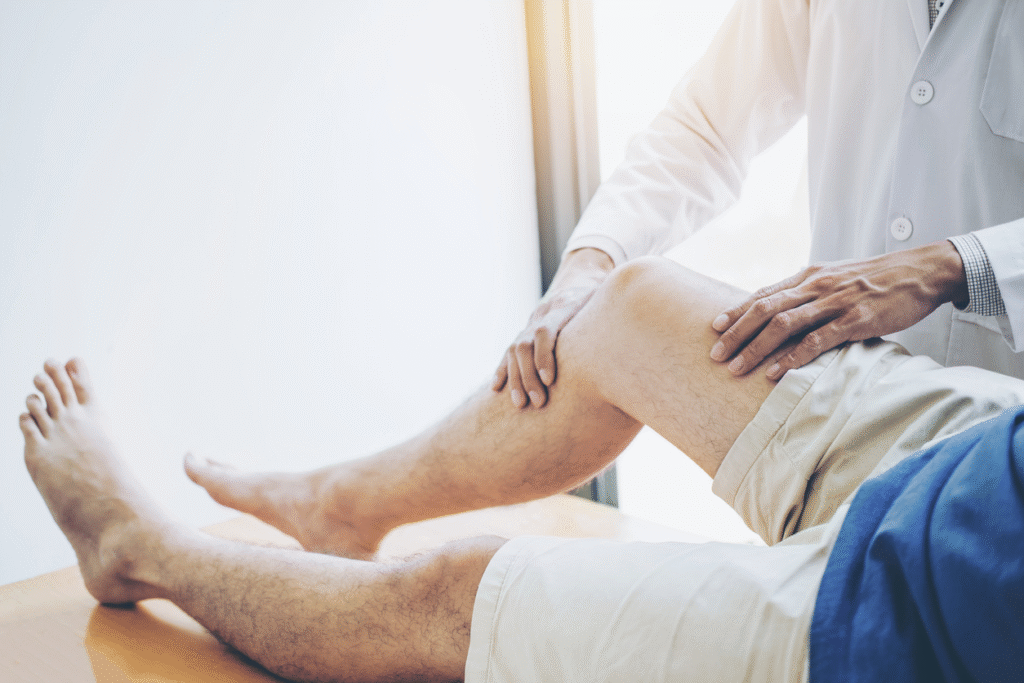
Definition Osteoarthritis Management
Inflammation of joints due to abnormality of articular cartilage is called Osteoarthritis.
আর্টিকুলার কার্টিলেজের অস্বাভাবিকতার কারণে জয়েন্টের প্রদাহকে অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস বলে।
Osteoarthritis Management
The management of osteoarthritis (OA) is a comprehensive subject focusing on alleviating pain, improving functional status, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. This subject is multidisciplinary, integrating lifestyle modifications, physical therapies, medications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions, with core treatments being non-pharmacological. The management approach is highly individualized, considering the affected joints, pain severity, comorbidities, and patient preferences.
Core Principles of Osteoarthritis Management
The primary philosophy in managing OA is to start with the safest and least invasive therapies and only progress to more invasive options when necessary.
- Patient Education and Self-Management: A foundational element involves educating patients about their condition, countering misconceptions (e.g., that pain always means harm, or that the condition is untreatable), and empowering them to manage their symptoms actively. This includes shared decision-making in developing a personalized care plan.
- Holistic Assessment: Management plans take into account the patient’s overall well-being, including psychosocial components, occupation, mood, and relationships, as chronic pain and mobility issues can have significant impacts.
- Graded Approach: Treatment typically follows a stepped approach, beginning with non-pharmacological methods and adding pharmacological or surgical interventions only when symptoms persist or worsen.
Key Management Strategies for Osteoarthritis Management
The subject of osteoarthritis management can be broadly divided into three main categories: non-pharmacological, pharmacological, and surgical interventions.
Non-Pharmacological Management (Core Treatments)
These are the cornerstones of therapy and should be offered to all patients, irrespective of age or disease severity.
- Exercise and Physical Activity: Tailored therapeutic exercise, including local muscle strengthening and general aerobic fitness (e.g., walking, swimming, cycling, tai chi), is crucial for maintaining joint flexibility, strengthening surrounding muscles, reducing pain, and improving function. Water aerobics or hydrotherapy is particularly useful for those with severe pain due to its low-impact nature.
- Weight Management: For individuals who are overweight or obese, losing weight significantly reduces stress on weight-bearing joints (like the knees and hips) and can lessen pain and potentially slow cartilage loss. Even modest weight loss yields benefits.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: Referrals to physical therapists (PT) and occupational therapists (OT) are vital. PTs develop exercise programs and teach proper movement mechanics, while OTs provide strategies for daily activities (ADLs), joint-protection techniques, and may recommend assistive devices.
- Supportive Devices: Canes, walkers, appropriate footwear with shock-absorbing soles, splints for hand or thumb OA, and braces can help offload pressure, stabilize joints, improve mobility, and reduce fall risk.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Applying hot packs (to ease stiffness and relax muscles) or cold packs (to reduce swelling and pain after activity) can provide symptomatic relief for some individuals.
Pharmacological for Osteoarthritis Management
Medications are used as adjuncts to core treatments to manage pain, typically at the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration.
- Topical Analgesics: Topical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like diclofenac gel are often the first-line pharmacological treatment for knee and hand OA, as they provide pain relief with minimal systemic side effects. Capsaicin cream is another topical option.
- Oral Analgesics and NSAIDs: If topical treatments are insufficient, oral medications may be considered.
- Acetaminophen (paracetamol) can be tried for mild to moderate pain, although its effectiveness is debated in some guidelines.
- Oral NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen, celecoxib) are generally more effective than acetaminophen for moderate to severe pain but carry risks of gastrointestinal, renal, and cardiovascular issues. They are often prescribed with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) for stomach protection.
- Injections: Intra-articular corticosteroid injections can offer rapid, short-term relief (several weeks to months) from pain and inflammation during flare-ups. Hyaluronic acid injections (viscosupplementation) are another option for the knee, potentially offering longer relief, though evidence is mixed and controversial.
- Other Medications: Duloxetine, an antidepressant also approved for chronic pain, may be used in some cases. Opioids like tramadol are generally reserved for severe, intractable pain and short-term use due to side effect profiles and addiction potential.
- Supplements: Glucosamine and chondroitin are widely used, but studies show mixed or limited evidence of benefit; major guidelines generally do not recommend their routine use.
Surgical Interventions
Surgery is generally considered only when conservative non-pharmacological and pharmacological treatments fail to provide adequate pain relief and function is severely limited.
- Joint Replacement (Arthroplasty): Total hip or knee replacement is the most common and definitive procedure for advanced OA, providing significant pain relief and restoring function.
- Osteotomy: This procedure is primarily for younger, active patients with joint misalignment (e.g., in the knee or hip) and involves reshaping the bone to shift weight from the damaged to the healthier part of the joint, potentially delaying a total replacement.
- Arthroscopy: Procedures like arthroscopic lavage and debridement are not generally recommended for most OA cases unless specific mechanical locking is present due to loose bodies.
Conclusion
The subject of osteoarthritis management is extensive, emphasizing a tailored, holistic approach that prioritizes conservative measures. The focus is not on cure, as there is currently no disease-modifying medication, but on empowering patients to manage their symptoms effectively through an integrated approach. By combining lifestyle changes, physical therapies, and appropriate medications, individuals can significantly improve their function and quality of life. Emerging biological therapies and other research continue to explore new ways to manage or even slow the progression of this common condition. If you have further questions about specific treatments or aspects of care, please feel free to ask
Causes of Osteoarthritis Management
- Aging: Osteoarthritis is more common as people get older.
- Overweight and Obese: BMI is greater than 25 kg/Sq miter
- Overuse: Exessive hilling, Exessive lifting, Excessive cycling, etc.
- Injury and Surgery: Injury and Surgery can make the joint abnormal.
- Family history (Genetics): It may be due to genetic cause.
বার্ধক্য: মানুষের বয়স বাড়ার সাথে সাথে অস্টিওআর্থারাইটিস বেশি হয়। অতিরিক্ত ওজন এবং স্থূল: BMI 25 কেজি/বর্গ মিটারের বেশি অত্যধিক ব্যবহার: অতিরিক্ত হিলিং, অত্যধিক উত্তোলন, অত্যধিক সাইকেল চালানো ইত্যাদি। আঘাত এবং অস্ত্রোপচার: আঘাত এবং অস্ত্রোপচার জয়েন্টকে অস্বাভাবিক করে তুলতে পারে। পারিবারিক ইতিহাস (জেনেটিক্স): এটি জেনেটিক কারণে হতে পারে।
Clinical feature of Osteoarthritis Management
Pain in the affected joint
Stiffness of the affected joint
আক্রান্ত জয়েন্টে ব্যথা
আক্রান্ত জয়েন্টের দৃঢ়তা
আক্রান্ত জয়েন্ট ফুলে যাওয়া
আক্রান্ত জয়েন্টের সীমিত গতি
Laboratory Investigation of Osteoarthritis Management
Laboratory investigation of osteoarthritis
1. Blood for
a. CBC CP
b. RA
2. Urine RME
3. X-ray: Affected joint
অস্টিও আর্থ্রাইটিস এর ল্যাবরেটরি ইনভেস্টিগেশন লিখ।
অস্টিও আর্থ্রাইটিস এর ক্ষেত্রে ল্যাবরেটরি ইনভেস্টিগেশন
১. ব্লাড ফর
• সিবিসি সিপি
• আর.এ
২. ইউরিন: আর.এম.ই
৩. এক্সরে: আক্রান্ত সন্ধি
Treatment of Osteoarthritis Management
Treatment of osteoarthritis
General management
1. If obesity then reduce weight,
2. Calcium enriched diet.
3. Regular mild exercise
4. Hot compression of affected joint may be helpful.
Medication
1. Pain management
a. Topical NSAIDS
b. Oral NSAIDs; e.g. paracetamol, Ibuprophen, Naproxen etc.
c. Antidepressant: to reduce nocturnal pain; e.g. Amitriptyline.
2. Supplement
a. Calcium with Vitamin D
Physiotherapy.
অস্টিওআর্থাইটিস এর চিকিৎসা লিখ।
অস্টিওআর্থাইটিস এর চিকিৎসা
সাধারণ ব্যবস্থাপনা
১. স্থুলতা থাকলে ওজন কমাতে হবে।
২. ক্যালসিয়াম সমৃদ্ধ খাবার খেতে হবে।
৩. নিয়মিত মৃদু ব্যয়াম করতে হবে।
৪. আক্রান্ত জয়েন্টে গরম সেক দেয়া যেতে পারে।
ঔষধজ চিকিৎসা
১. বেদনা কমানোর জন্য
টপিক্যাল এনএসএআইডি।
মুখে খাওয়ার বেদনা নাশক: প্যারাসিটামল, আইবুপ্রোফেন, ন্যাপ্রোক্সেন ইত্যাদি।
এন্টিডিপ্রেসেন্ট; রাতের বেদনা হ্রাস করার জন্য, যেমন এমিট্রিপটাইলিন।
২. সাপ্লিমেন্ট: ক্যালসিয়াম ও ভিটামিন ডি
ফিজিওথেরাপী।
Swelling of the affected joint Limited motion of the affected joint
Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis Management
A physical examination & lab tests help to make up the diagnosis.
- Joint aspiration: A needle is inserted into the joint to pull out fluid.
- X- Ray: X-ray can show joint or bone damage or changes related to osteoarthritis.
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) gives a better view of cartilage & other parts of the joint.
Pain relief medicines for Osteoarthritis Management
Sometimes a combination of therapies such as painkiller, exercise & surgery may be help control your pain. The main medications used are below such as –
- Paracetamol
If you have pain caused by osteoarthritis, your GP (General Practitioners) might suggest consider taking paracetamol for short term pain relief.
- NSAID
These are painkiller reducing inflammation such as creams. Some NSAIDs are available without a prescription. They can be particularly effective if you have osteoarthritis in your knees or hands.
- Opioids
Opioids such as codeine are another type of painkiller that may help relieve severe pain
- Steroid Inj
Steroids are a type of medication that contain manmade versions of the hormone cortisol & some times used to treat particularly painful musculoskeletal problems. Steroid inj work quickly & can ease pain for several weeks or months.
- Hot or cold packs
Hot & cold packs to the joints can relive the pain & symptoms of osteoarthritis in some people. A hot water bottle filled with either hot or cold water & applied to the affected area can be very effective in reducing pain.
- Assistive devices
If osteoarthritis is causing mobility problems or making it difficult to do everyday tasks, several devices could help.
- Manual therapy
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka