Paramedical 2 Years Course Details
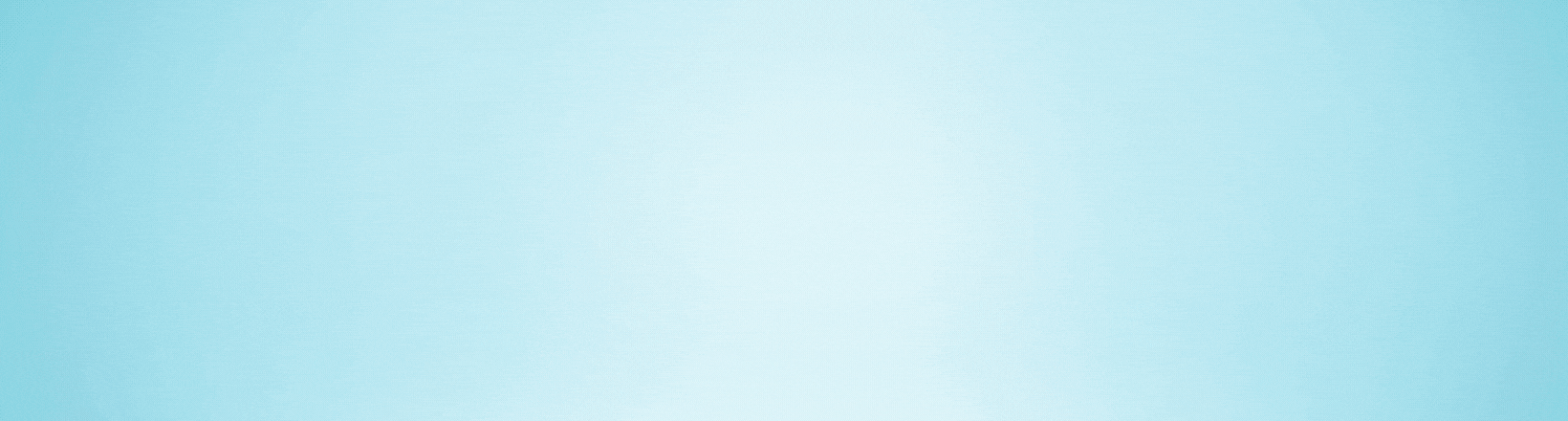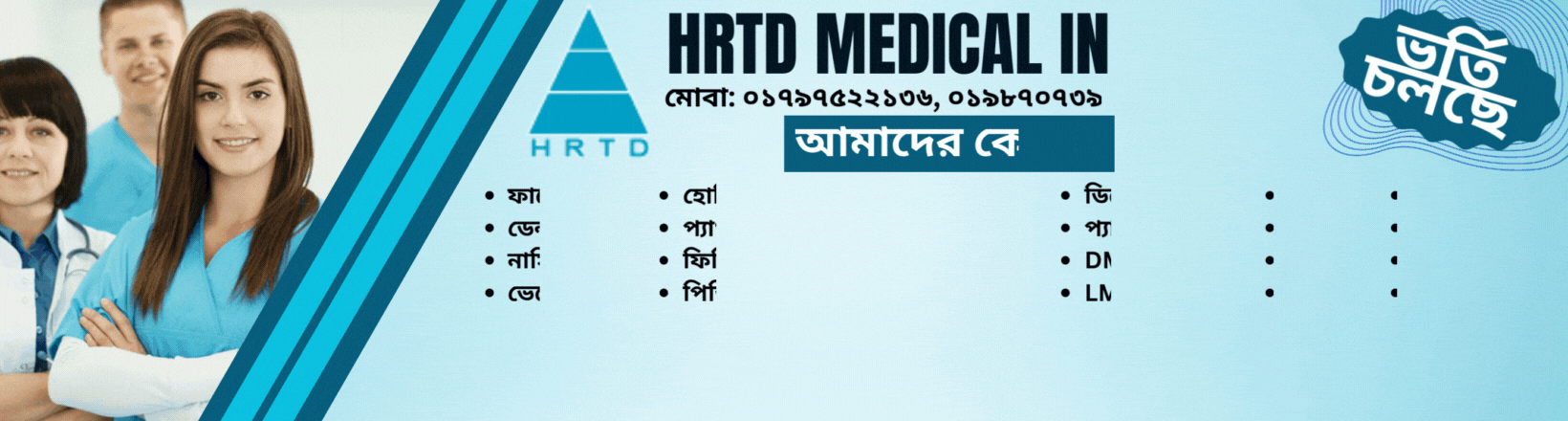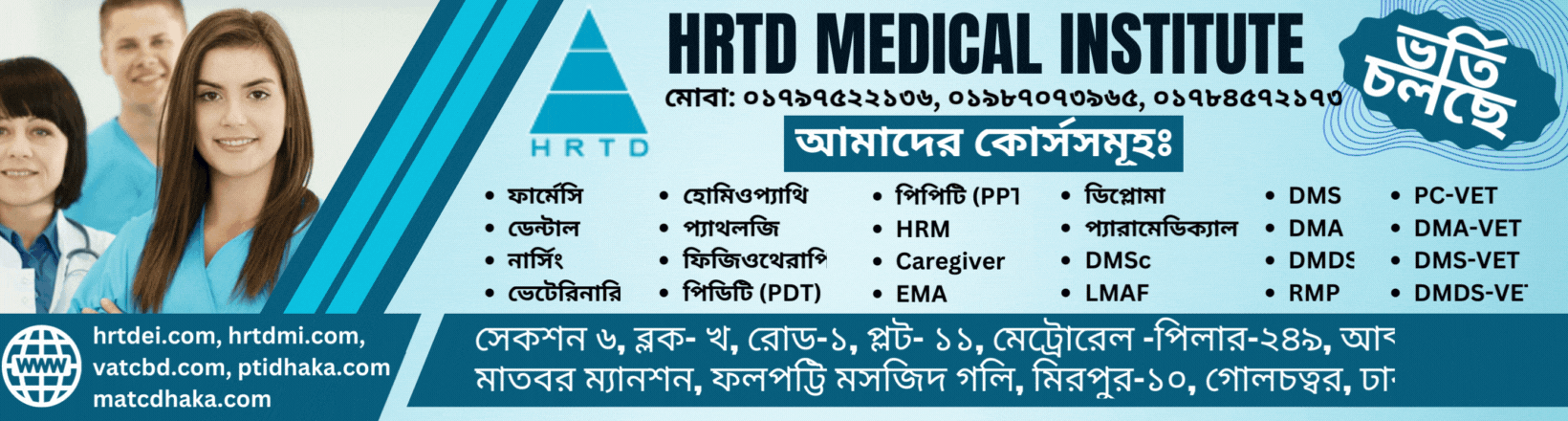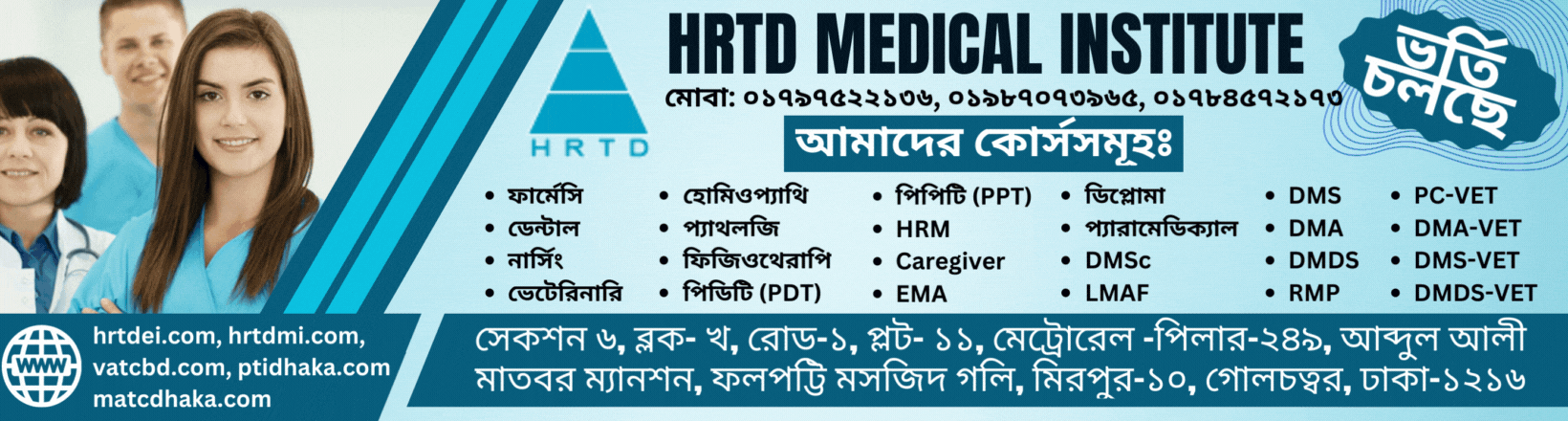
Paramedical 2 Years Course is a long paramedical course in Bangladesh. This Course is available in HRTD Medical Institute. HRTD Medical Institute is reputed and popular for Paramedical Courses, Pharmacy Courses, Diploma Medical Assistant Courses, etc. HRTD Medical Institute is an organization of HRTD Limited which is Registered by the Govt of the People Republic of Bangladesh.

Total Cost for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Total Cost =92500 tk
Admission fee =16500 tk
Monthly fee (3000×24) = 72000 tk
Exam fee ( 1000×4) =4000 tk
Location of Paramedical 2 Years Course
HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Folpotty Mosjid Goli (Bitul Mamur Jame Mosjid Goli), Plot No. 11, Metro Rail Piller No. 249, Mirpur 10 Golchattar, Dhaka.
Class System for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Class System for Paramedical 2 Years Course in Dhaka : Weekly Class 3 hours. For Job holders 3 hours in a day. The option days are Friday Morning Shift from 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, Friday Evening Shift from 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM, Monday Morning Shift from 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, Monday Evening Shift from 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM. Saturday Morning Shift from 10am to 1 Pm, Evening Shift from 3 pm to 6 pm.
For Regular Students Saturday 1 hour, Monday 1 hour, and Friday 1 hour. Morning Shift From 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, and Evening Shift From 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM.
Subjects for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Human Anatomy and Physiology
- Pharmacology
- First Aid
- Study of OTC Drugs
- Practice of Medicine-1
- Hematology and Pathology
- Microbiology and Antimicrobial Drugs
- Study of Gastrology
- Study of Cardiology
- Study of Orthopedics
- Surgery
- Neuro Anatomy
- General Pathology-1
- General Chemistry & Biochemistry
- Community Medicine
Teacher for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Dr. Sakulur Rahman, MBBS, PGT, CCD
- Dr. Shamima, MBBS
- Dr. Disha, MBBS
- Dr. Tisha, MBBS
- Dr. Sanjana, BDS
- Dr. Juthi, BDS
- Dr. Keya, BDS
- Dr. Mahinul Islam, MBBS
- Dr. Antora, MBBS
- Dr. Turzo, MBBS
Practical Class for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Practical Works. Mobile Phone 01797522136, 01987073965. There are many practical works in the Paramedical 4 Years Course. The Practical works are Heart Beat, Heart Rate, Pulse, Pulse Rate, Weak Pulse, Strong Pulse, Atrial Beat, Ventricular Beat, Tachycardia, Bradycardia, Arrhythmia, Heart Sound, Normal Heart Sound, Abnormal Heart Sound, Cardiac Mur Mur, Blood Pressure, Systolic Blood Pressure, Diastolic Blood Pressure, Pulse Pressure, Mean Blood Pressure.
Hypertension, Hypotension, Hypertension Emergency, Management of Hypertension, Management of Hypotension, Management of Hypertension Emergency, IM Injection, IV Injection, SC Injection, ID Injection, Saline Pushing, Application of Eye Drops, Application of Pediatric Medicine, Emergency Respiratory Drugs, Use of Inhaler, Use of Ratahaler, Use of Nebulizer.
BMI, Normal Body Weight, Under Weight, Over Weight, Obesity, Cleaning, Dressing, Bandaging, Use of Mouth Anti Septic Mouth Wash, Use of Suppository, Use of Eye Drops, Use of Ear Drops, Use of Skin Ointment and Cream, Canulla Setting, Post Surgical Cleaning, Post Surgical Dressing, Post Surgical Bandaging, Post Surgical Pain Management. Roller Bandage, Triangular Bandage.
Making Suspension from PFS, Making Solution from ORS, Auscultation, Auscultation of Thorax, Respiratory Auscultation, Abdominal Auscultation, Percussion, Appendicitis Pulpation, Prescription Understanding, Report Understanding, X-Ray Report Understanding, Blood Test Report Understanding, Urine Test Report Understanding, ECG Report Understanding, Echo Report Understanding, ETT Report Understanding.
Human Anatomy and Physiology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Human Anatomy & Physiology (A&P) studies the body’s structure (Anatomy: the “what” and “where”) and function (Physiology: the “how”). Anatomy covers physical parts from cells to systems (like skeletal, nervous, circulatory), while Physiology explains how these structures work together to maintain life, focusing on processes like movement, metabolism, and homeostasis (internal balance). Together, A&P explains how the body’s form dictates its function, from microscopic cell activity to complex organ system interactions, crucial for understanding health and disease.
Anatomy: The Study of Structure
- Definition: The study of the body’s physical structures and their relationships.
- Levels: Can be studied at various scales:
- Gross Anatomy: Large structures visible to the naked eye (organs, limbs).
- Microscopic Anatomy (Histology): Tissues, cells, and organelles.
- Branches: Includes gross, microscopic, developmental (embryology), regional, and clinical anatomy.
Physiology: The Study of Function
- Definition: The study of how body parts work and support life processes.
- Focus: Explains the physical and chemical processes (like nerve impulses, muscle contractions) that occur within structures.
- Key Concept: Homeostasis: Maintaining stable internal conditions (e.g., body temperature, blood sugar).
- Branches: Includes neurophysiology (nerves), cardiovascular physiology (heart), and pharmacology (drug effects).
The Interrelationship: Form Meets Function
- Anatomy and physiology are inseparable; structure dictates function.
- Example: The hand’s finger shape and joints (anatomy) allow it to grasp objects (physiology).
- Example: The heart’s chambers and valves (anatomy) enable it to pump blood (physiology).
Major Body Systems (Brief Overview)
- Integumentary: Skin, hair, nails (protection).
- Skeletal/Muscular: Bones, muscles (movement, support).
- Nervous: Brain, spinal cord, nerves (communication).
- Circulatory: Heart, blood vessels (transport).
- Respiratory: Lungs, airways (gas exchange).
- Digestive: Stomach, intestines (nutrient absorption).
- Urinary/Reproductive/Endocrine/Lymphatic: Other vital systems for waste, hormones, immunity, etc..
Pharmacology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Pharmacology is the scientific study of drugs and their effects on living systems, exploring how chemicals interact with the body to treat, prevent, or cause disease, covering drug discovery, development, mechanisms (pharmacodynamics), body processing (pharmacokinetics: ADME), toxicology, and therapeutic use, bridging biology, chemistry, and medicine for careers in research, healthcare, or industry.
Key Areas of Study for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Pharmacokinetics (PK): What the body does to the drug (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion – ADME).
- Pharmacodynamics (PD): What the drug does to the body (mechanism of action, cellular effects).
- Drug Development: Discovery, design, testing, and approval of new medicines.
- Toxicology: The harmful effects and safety of chemical substances.
- Therapeutics: How drugs are used to manage diseases.
What You Learn
- How drugs interact with molecular targets (receptors, enzymes).
- Biochemical processes for effective drug concentrations.
- Effects on various organ systems and disease states.
- Factors influencing drug response (genetics, age, disease).
- Ethical, legal, and economic aspects of drug use.
Related Fields & Career Paths
- Interdisciplinary: Combines chemistry, biology, medicine, physiology, and genetics.
- Career Focus: More research-oriented than Pharmacy, leading to roles in drug discovery, clinical research, academia, or regulatory affairs, rather than dispensing.
First Aid 1&2 for Paramedical 2 Years Course
First Aid Levels 1 & 2 are progressive training stages, with Level 1 focusing on Basic Life Support (BLS) for everyday emergencies (CPR, bleeding, burns, choking) in low-risk settings, while Level 2 builds on this with Intermediate Life Support (ILS), adding skills like splinting, bandaging, and managing more complex injuries (head/spinal, multiple injuries) for higher-risk environments, often combined into one comprehensive course.
First Aid Level 1 (Basic Life Support)
- Focus: Essential, immediate response to common emergencies.
- Topics: Scene safety, CPR & AED basics, choking, bleeding/wounds, burns, shock, fainting, basic fractures.
- Best For: General staff, offices, schools (low-risk).
First Aid Level 2 (Intermediate Life Support)
- Focus: Advanced skills beyond basic life support, building on Level 1.
- Topics: More detailed splinting/bandaging, managing head/spinal injuries, multiple injuries, vital signs, patient history, poisons/bites, rescue carries, drowning, asthma, heart attacks.
- Best For: Higher-risk workplaces needing more comprehensive care before professionals arrive.
Combined Level 1 & 2 Training
- Often offered together to avoid repetition, providing a complete intermediate skill set.
- Includes anatomy/physiology basics to understand why treatments work.
In essence, Level 1 teaches you to handle the basics, while Level 2 teaches you to handle more complex situations and provide better ongoing care until paramedics arriv
Study of OTC Drugs for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Studying Over-the-Counter (OTC) Drugs involves understanding their pharmacology, safe use, prevalence, misuse, and influencing factors (like convenience, cost, education), covering common types like analgesics, antacids, and cough suppressants, with a focus on risks such as masking serious conditions, antibiotic resistance, and potential for abuse (like DXM/loperamide). Key areas include self-medication trends, knowledge gaps in the public (even in health students), and the need for better regulation and education to manage risks and promote responsible self-care.
Key Aspects of OTC Drug Study for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Pharmacology & Chemistry: Understanding how these drugs work, their active ingredients (e.g., acetaminophen, ibuprofen, dextromethorphan), solubility, formulation, and how the body processes them (dosing, half-life).
- Self-Medication Practices: Investigating why people use OTCs, common motivations (convenience, cost, time), and patterns of use across different populations (students, general public).
- Knowledge & Awareness: Assessing public understanding of safe usage, side effects, interactions, and expiry dates, often revealing significant gaps.
- Risks & Misuse: Studying overuse, misuse (e.g., “robo-tripping” with DXM), potential for addiction (loperamide), masking severe illnesses, and promoting antimicrobial resistance.
- Regulatory & Policy: Examining how OTC drugs are controlled and the need for effective strategies to improve safety and access.
Common OTC Drug Categories & Examples for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Analgesics/Antipyretics: Pain relievers (acetaminophen, ibuprofen) and fever reducers.
- Antacids: For indigestion.
- Cough & Cold Meds: Cough suppressants (Dextromethorphan – DXM), decongestants, antihistamines.
- Anti-diarrheals: Loperamide.
Why Study OTC Drugs?
- Public Health: OTCs are integral to minor health management, but their misuse poses risks.
- Education: To bridge knowledge gaps, particularly among young people and students who self-medicate heavily.
- Safety: To prevent overdose, adverse effects, and complications from improper use.
In essence, studying OTC drugs balances recognizing their utility for minor ailments with addressing the significant health implications of unsupervised use, driving research into better education and regulation.
Practice of Medicine-1 for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Practice of Medicine-1 (PoM-1) is usually a foundational medical course, especially in Homoeopathy (BHMS/MD), focusing on the art of diagnosis, understanding systemic diseases (respiratory, digestive, endocrine, infectious), clinical skills, patient communication, and integrating basic sciences with homeopathic principles for effective patient management, often covering core topics like clinical methods, basic pathology, and evidence-based practice.
Key Areas Covered in PoM-1 for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Clinical Skills: Physical examination, diagnostic procedures, case history taking, and developing empathy.
- Systemic Diseases: Focus on respiratory, digestive (liver, peritoneum), endocrine, and metabolic disorders, often with infectious/tropical diseases.
- Basic Sciences Application: Linking anatomy, physiology, and pathology to clinical scenarios.
- Homoeopathic Integration: Applying homeopathic philosophy (miasmatic study, principles) to clinical presentations and remedies (therapeutics).
- Patient Management: Ethics, communication, managing emergencies, and understanding socio-cultural factors in health.
Typical Syllabus Breakdown
- Paper I (Often): Respiratory, Digestive, Blood, Tropical Diseases, plus Homoeopathic Therapeutics for these systems.
- Paper II (Often): Cardiovascular, Locomotor, Urino-genital, Nervous, Psychological Medicine, Pediatrics, and related Therapeutics.
- Common Topics: Infectious diseases, nutritional/metabolic disorders, clinical genetics, immunology basics, and public health.
Purpose of the Subject
- To build a strong foundation for diagnosing and treating patients using a holistic, evidence-based approach.
- To prepare students for advanced clinical practice and professional examinations.
Hematology and Pathology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Hematology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Hematology is the branch of medicine and science focused on the study, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of blood, blood-forming organs (like bone marrow), and blood disorders, covering everything from red/white blood cell/platelet issues to clotting problems and blood cancers like leukemia, involving both lab analysis (hematopathology) and patient care (hematologists). Key areas include blood counts, morphology (cell appearance), and hemostasis (clotting), with subjects like anemia, sickle cell, hemophilia, and lymphoma falling under its scope.
What Hematology Covers for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Blood Components: Red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), platelets (thrombocytes), plasma, hemoglobin, blood proteins.
- Blood-Forming Organs: Bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes, thymus.
- Disorders & Diseases:
- Anemias: Iron deficiency, sickle cell anemia.
- Cancers: Leukemia, lymphoma, multiple myeloma.
- Bleeding/Clotting Disorders: Hemophilia, thrombosis (blood clots).
- Infections: Affecting blood cells.
- Processes: Hemopoiesis (blood cell formation), coagulation (clotting).
Key Roles
- Hematologist: A doctor diagnosing and treating patients with blood disorders, often in consultation or a combined practice with oncology (hematology-oncology).
- Hematopathologist: A doctor specializing in laboratory diagnosis of blood diseases, examining tissues and blood samples.
- Medical Laboratory Scientist: Performs the lab tests (blood counts, morphology) that are crucial for diagnosis.
Why It’s Important
Hematology helps diagnose common conditions like anemia, infections, and clotting issues, as well as complex blood cancers, making it a vital field in medicine and medical laboratory science
Pathology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Pathology is the medical subject focused on the study of diseases—their causes (etiology), mechanisms (pathogenesis), and effects (structural/functional changes) on the body, bridging basic sciences and clinical medicine for accurate diagnosis and treatment. It involves analyzing body fluids, tissues, and cells (histopathology, cytopathology, molecular pathology) to understand illnesses like cancer, infections, and genetic disorders, and is crucial for guiding patient care and research.
Key Areas of Pathology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Anatomical Pathology: Examines tissues (biopsies, surgical specimens) and cells to diagnose disease (e.g., cancer).
- Clinical Pathology: Analyzes body fluids like blood, urine, and bone marrow for chemical, hematological, and microbiological indicators of disease.
- Molecular Pathology: Studies diseases at the molecular level, using genetic and protein analysis for diagnosis.
- Microbiology: Focuses on infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, fungi).
What It Covers (Curriculum)
- General Pathology: Basic concepts like cell injury, inflammation, and neoplasia (tumors).
- Systemic Pathology: How specific diseases affect different organ systems.
- Diagnostic Techniques: Gross (macroscopic) and microscopic analysis, immunohistochemistry, Pap smears, etc..
- Autopsy: Post-mortem examination to determine cause of death.
Why It’s Important
- Diagnosis: Provides definitive diagnoses that guide treatment.
- Prognosis: Helps determine disease severity and likely outcome.
- Research: Advances understanding of disease and develops new therapies.
- Foundation: Essential for understanding all other medical disciplines.
Career Paths
- Physician Pathologist: A medical doctor specializing in pathology.
- Clinical Scientist: Works in labs, performing advanced tests and research.
- Medical Lab Technician: Performs routine tests in labs.
In essence, pathology is the “science behind the cure,” interpreting what’s happening inside the body to help other doctors treat patients effective
Microbiology and Antimicrobial Drugs for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Microbiology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Microbiology is the scientific study of microscopic organisms (microbes) like bacteria, viruses, fungi, archaea, and protozoa, exploring their structure, function, classification, and interactions with environments and hosts, crucial for understanding life, disease (pathogens), medicine, agriculture, and biotechnology, with branches including bacteriology, virology, mycology, and immunology. It involves studying how these tiny life forms impact health, food safety, and the planet, using techniques from molecular biology to environmental science.
Core Concepts
- Microorganisms: Bacteria, viruses, fungi, algae, protozoa, archaea.
- Scope: Structure, function, genetics, evolution, ecology, and control of microbes.
- Importance: Disease prevention, vaccine development, food production, environmental health.
Key Branches
- Bacteriology: Study of bacteria.
- Virology: Study of viruses.
- Mycology: Study of fungi.
- Immunology: Study of the immune system and microbial responses.
- Microbial Ecology: Microbes in their natural environments.
- Medical Microbiology: Pathogens and infectious diseases.
- Food Microbiology & Agricultural Microbiology: Microbes in food and farming.
Typical Subjects in a Microbiology Course for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- General Microbiology & Microbial Diversity
- Biochemistry & Microbial Metabolism
- Molecular Biology & Genetics
- Cell Biology & Physiology
- Virology, Mycology, & Parasitology
- Immunology
- Bioinformatics & Biostatistics
- Microbial Techniques & Quality Control
Applications
- Healthcare: Diagnosing infections, developing antibiotics, creating vaccines.
- Industry: Fermentation (beer, yogurt), biotechnology, pharmaceuticals.
- Environment: Bioremediation, understanding nutrient cycles.
Study of Gastrology for Paramedical 2 Years Course
The study of Gastroenterology (or Gastroenterology) is the branch of medicine focused on the entire digestive system—from the mouth to the anus, including the esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, and bile ducts—and its disorders, covering normal function, diseases (like GERD, IBS, IBD, hepatitis, ulcers, cancers), diagnosis (endoscopy, colonoscopy, biopsies), treatment, and research, blending clinical care with procedural skills and a growing focus on nutrition and the gut microbiome.
What it covers
- Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract: Mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus.
- Accessory Organs: Liver, gallbladder, pancreas, biliary tree.
- Functions Studied: Motility (movement), digestion, nutrient absorption, waste removal.
- Conditions Treated: Heartburn, ulcers, IBS, IBD (Crohn’s, Colitis), celiac disease, hepatitis, gallstones, pancreatitis, colon polyps/cancer, hemorrhoids, liver disease.
Key aspects of the study for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Procedures: Gastroenterologists perform endoscopic procedures (colonoscopy, endoscopy, ERCP, EUS) to visualize and treat issues internally.
- Diagnosis: Involves patient assessment, lab tests, imaging (X-rays, MRIs, CTs), and diagnostic procedures.
- Treatment: Manages both acute and chronic conditions, often involving medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes referring for surgery.
- Subspecialties: Includes areas like hepatology (liver), IBD, advanced endoscopy, and gut microbiome research.
- Interdisciplinary Links: Connects with neurology (brain-gut axis), nutrition, and surgery.
How to study it (as a career path)
- It’s a competitive subspecialty of Internal Medicine, requiring extensive post-medical school training (fellowship) after MBBS/MD.
- It offers a blend of complex medical knowledge, procedural skills, and patient care, with opportunities in hospitals, clinics, and research.
Study of Cardiology For Paramedical 2 Years Course
Cardiology is the medical study of the heart and blood vessels (cardiovascular system), focusing on diagnosing, treating, and preventing conditions like heart attacks, heart failure, arrhythmias, and congenital defects, involving anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and advanced diagnostics like ECGs & echocardiograms, with pathways to specialization (e.g., Interventional, Pediatric) after core medical training.
What Cardiology Covers for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Core Focus: Heart and circulatory system disorders, from coronary artery disease (CAD) to heart failure and valve diseases.
- Key Areas: Electrophysiology (heart rhythms), cardiac imaging, pharmacology, rehabilitation, and emergency care.
- Sub-Specialties: Pediatric Cardiology, Interventional Cardiology (procedures), Preventive Cardiology, Cardiac Imaging.
Key Subjects & Skills:
- Foundational: Anatomy, Physiology, Biochemistry, Pharmacology.
- Diagnostic: ECG (Electrocardiography), Echocardiography (ultrasound), Cardiac Catheterization, Angiography.
- Clinical: Heart Failure Management, Arrhythmia Treatment, Cardiac Rehabilitation, Genetics.
How to Study Cardiology (Pathways):
- Medical Degree (MBBS/MD): Complete general medical training.
- Residency: Specialize in Internal Medicine.
- Fellowship/Specialization: Further sub-specialize in Cardiology (e.g., DM in India, Fellowship in other countries).
- BSc/MSc Options: Also available for specialized cardiac science training, often alongside or after 12th grade, focusing on diagnostics and care.
Why It’s Important:
Cardiovascular diseases are a leading cause of death globally, making cardiology crucial for public health, improving quality of life, and managing complex conditions.
Study of Orthopedics for Paramedical 2 Years Course
Studying orthopedics involves the in-depth diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of musculoskeletal system disorders (bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves) through surgical and non-surgical methods, covering trauma (fractures), degenerative diseases (arthritis), sports injuries, and deformities, with advanced training leading to subspecialties like spine, sports medicine, or joint reconstruction, requiring extensive medical education and residency.
Core Focus Areas for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Anatomy & Physiology: Deep understanding of the musculoskeletal system (bones, joints, muscles, etc.).
- Trauma: Managing fractures, dislocations, and acute injuries.
- Degenerative Conditions: Treating wear-and-tear issues like osteoarthritis, often with joint replacements.
- Sports Injuries: Addressing ligament tears (ACL), tendon injuries (rotator cuff), and other athletic-related problems.
- Spinal Disorders: Conditions like scoliosis, disc issues, and nerve compression.
- Pediatrics: Congenital conditions (clubfoot) and growth-related issues.
- Imaging: Using X-rays, MRI, CT scans for diagnosis.
What You Study (Topics)
- Fractures & Dislocations
- Bone & Joint Diseases/Tumors
- Congenital Anomalies
- Nerve Injuries & Compression (e.g., Carpal Tunnel)
- Soft Tissue Injuries (tendons, ligaments)
Path to Becoming an Orthopedist
- MBBS/Medical School: Foundational medical degree (e.g., MBBS in India, MD in the US).
- Internship/Residency: General surgical internship followed by a specialized orthopedic surgery residency (around 4-5 years).
- Fellowship (Optional): Further specialization in areas like Hand Surgery, Spine, Sports Medicine, or Trauma.
Subspecialties
- Sports Medicine: Focus on athletes.
- Spine Surgery: Treating spine conditions.
- Joint Replacement: Hip, knee, shoulder reconstruction.
- Hand & Foot Surgery: Specific conditions in these extremities.
- Pediatric Orthopedics: Children’s musculoskeletal health.
Key Goal
To restore function, reduce pain, and improve the quality of life for individuals with musculoskeletal problems, from acute emergencies to chronic conditions, using advanced techniques and technology
Surgery for Paramedical 2 Years Course
A “surgery subject” refers to the broad medical field treating conditions with manual/instrumental techniques, encompassing core principles (anatomy, wound healing, shock) and numerous specialties like General, Orthopedic, Neurosurgery, Cardiology, Urology, and Plastic Surgery, forming a key part of medical education (MBBS) leading to specialized training (MS/MCh).
Core Surgical Principles & Topics for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- Fundamentals: Anatomy, Physiology, Pathology, Wound Healing, Shock, Metabolism, Nutrition, Immunology, Resuscitation.
- Management: Antibiotics, Pain Management, Fluid Management, Trauma Care, Surgical Oncology, Intensive Care.
- Procedures: Suture Techniques, Minor Procedures, Basic Life Support, Emergency Care.
Major Surgical Specialties (Examples)
- General Surgery: Broad core knowledge, abdominal issues, breast, HPB (Hepato-Pancreato-Biliary).
- Orthopaedic Surgery: Bones, joints, limbs (shoulder, arm, etc.).
- Cardiothoracic Surgery: Heart and chest.
- Neurosurgery: Brain, spine, nerves.
- Vascular Surgery: Arteries, veins, circulation.
- Urology: Kidneys, bladder, urinary tract.
- Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery: Burns, wounds, aesthetic alteration, hand trauma.
- ENT (Otolaryngology): Ear, nose, throat.
- Pediatric Surgery: Surgery for children.
How it Fits in Medical Training (MBBS)
- Pre-Clinical: Foundational sciences like Anatomy, Physiology.
- Clinical Rotations: Hands-on experience in hospitals during MBBS, including General Surgery.
- Internship: Practical experience in various departments, including Surgery.
- Postgraduate: Specialization through Master of Surgery (MS) or other advanced degrees.
Neuro Anatomy for Paramedical 2 Years Course
- General Pathology-1
- General Chemistry & Biochemistry
- Community Medicine
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka