Mobile Number 01797522136, 01987073965.This Course is available in HRTD Medical Institute. HRTD Medical Institute is reputed and popular for 3 Years DMA Course, Pharmacy Courses, Diploma Medical Assistant Courses, etc. HRTD Medical Institute is an organization of HRTD Limited which is Registered by the Govt of the People Republic of Bangladesh. In Dhaka, you can pursue pharmacy education through various institutions offering diploma and degree programs. These programs range from short-term courses like a 3-month or 6-month pharmacy technician course to longer degree programs like a Bachelor of Pharmacy (Hons).

Short-Term Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
- Duration: 3 months, 6 months
- Focus: Practical skills for working in pharmacies, including dispensing medications and providing basic healthcare advice.
- Institutions: HRTD Medical Institute offers several such courses.
- Subjects: May include Human Anatomy & Physiology, Pharmacology, First Aid, and OTC Drugs.
- Cost: Varies depending on the duration and institution, but generally includes admission, monthly, and exam fees.
- Example: A 3-month course at HRTD Medical Institute may cost around Tk 18,500.
To find a Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
- Identify your desired level of study: Do you prefer a short technician course or a degree program?
- Research institutions: Look into universities offering pharmacy degrees and institutes offering technician courses.
- Contact institutions directly: For specific details about courses, fees, and admission requirements, contact the institutions. ,
- Consider location: HRTD Medical Institute is located in Mirpur-10.
- Explore options: Check for courses like C-Grade Pharmacist or Pharmacy Technician
Total Cost of 3 Months Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Pharmacy Course in Dhaka 3 months pharmacy course total cost 18500 taka, Admission fee 10500 taka, Monthly fee 2000 taka, Exam fee 2000 taka
Total cost of 3 months pharmacy course
Total cost-18500 tk
Admission fee-10500 tk
Monthly fee- (3×2000) =6000 tk
Exam fee-2000 tk
Total Cost of 6 Month Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
6 months pharmacy course total cost 30500 tk, Admission fee 10500 tk, Monthly fee 3000 tk, Exam fee 2000 tk.
Total cost of 6 months pharmacy course
Total cost-30500 tk
Admission fee-10500 tk
Monthly fee- (6×3000) =18000 tk
Exam fee-2000 tk
Total cost of 1 Year Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
1 Year pharmacy course total cost 52500tk, Admission fee 10500 tk, Monthly fee 3000 tk, Exam fee 2000 tk.
Total cost – 52500 tk
Admission fee- 10500 tk
Monthly fee (3000×12) =36000 tk
Exam fee (3000×2) =6000 tk
Document for Admission in Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Pharmacy Course in Dhaka Photocopy of Certificate, Photocopy of NID, Passport Size Photo 4 Pcs. Without NID, a Birth Certificate is allowed for an emergency case.
Admission Eligibility for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Pharmacy Course in Dhaka Admission Eligibility. Mobile Number. 01987073965. 01941123488, 01797522136. SSC or Equivalent/HSC/ Degree/Master’s from any Background (Science/ Arts/ Commerce/ Technical).
Class System for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Class System for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka : Weekly Class 3 hours. For jobholders, 3 hours a day. The option days are Friday Morning Shift from 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, Friday Evening Shift from 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM, Monday Morning Shift from 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, and Monday Evening Shift from 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM. Saturday Morning Shift from 10am to 1 Pm, Evening Shift from 3 pm to 6 pm.
For Regular Students, Saturday 1 hour, Monday 1 hour, and Friday 1 hour. Morning Shift From 9:00 AM to 12:00 PM, and Evening Shift From 3:00 PM to 6:00 PM.
Hostel Facilities in HRTD Medical Institute for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Hostel & Meal Facilities for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
The Institute has hostel facilities for the students. Students can take a bed in the hostel.
Hostel Fee Tk 3000/- Per Month
Meal Charges Tk 3000/- Per Month. ( Approximately )
হোস্টাল ও খাবার সুবিধা
ইনস্টিটিউটে শিক্ষার্থীদের জন্য হোস্টেল সুবিধা রয়েছে। ছাত্ররা হোস্টেলে বিছানা নিতে পারে।
হোস্টেল ফি 3000/- টাকা প্রতি মাসে,
খাবারের চার্জ 3000/- টাকা প্রতি মাসে।(প্রায়)
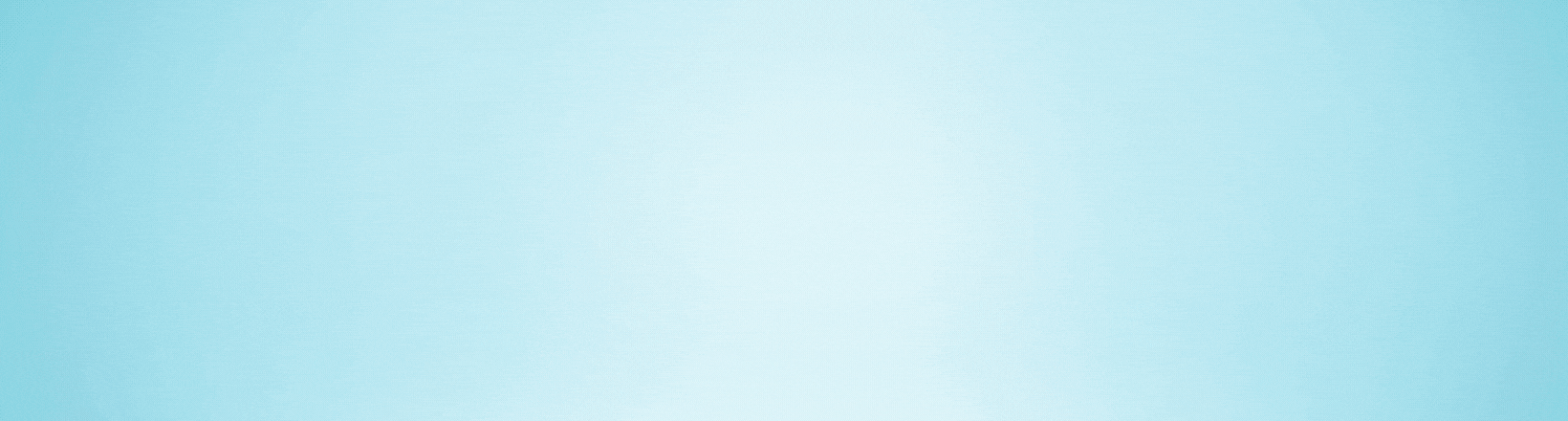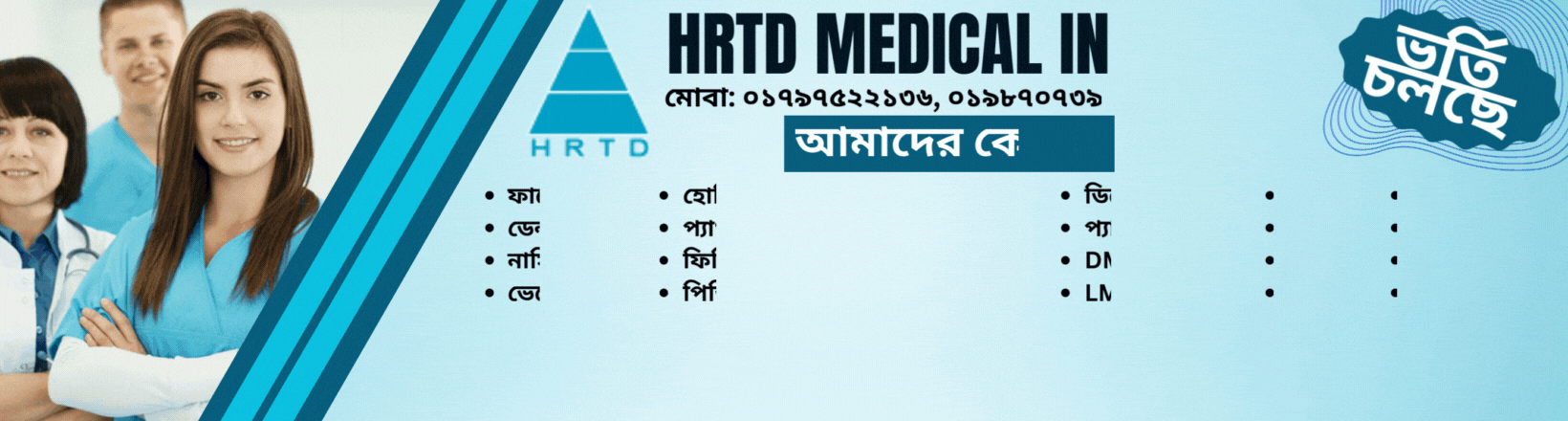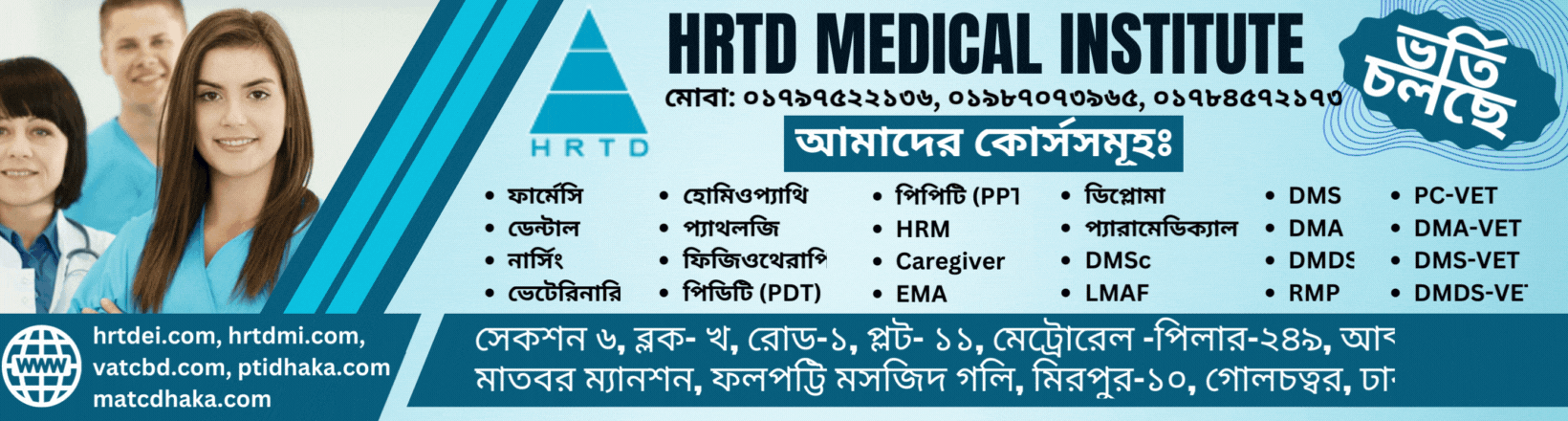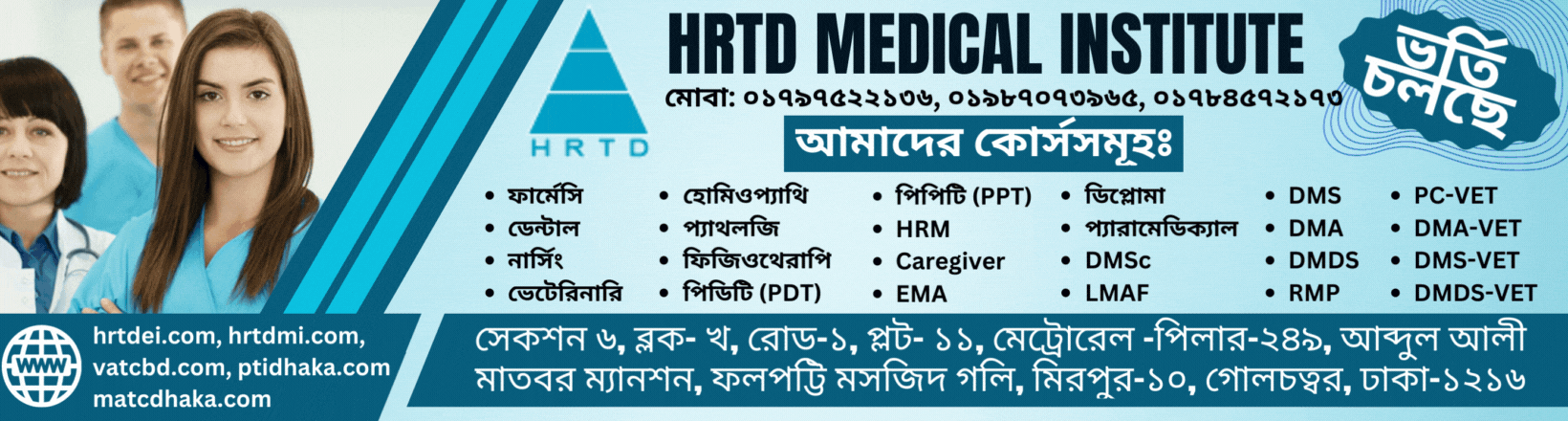
Address of HRTD Medical Institute for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
আমাদের ঠিকানাঃ HRTD মেডিকেল ইন্সটিটিউট, আব্দুল আলী মাদবর ম্যানশন, সেকশন ৬, ব্লোক খ, রোড ১, প্লট ১১, মেট্রোরেল পিলার নাম্বার ২৪৯, ফলপট্টি মসজিদ গলি, মিরপুর ১০ গোলচত্ত্বর, ঢাকা ১২১৬ । মোবাইল ফোন নাম্বার ০১৭৯৭৫২২১৩৬, ০১৯৮৭০৭৩৯৬৫ ।
Our Address: HRTD Medical Institute, Abdul Ali Madbor Mansion, Section-6, Block- Kha, Road- 1, Plot- 11, Metro Rail Pilar No. 249, Falpatty Mosjid Goli, Mirpur-10 Golchattar, Dhaka 1216. Mobile Phone No. 01797522136, 01987073965.
Total Subject & Total Marks of Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
1.Anatomy & Physiology -100 marks
2.Pharmacology-1 -100 marks
3.Sttudy of OTC drug -100 marks
4.First Aid & Antimicrobial drugs -100 marks
5.Pharmacology-2 -100 marks
Total Subject & Total Marks 2nd semester of Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
1.Cardiovascular drugs-100 marks
2.Essential drugs and medicines -100 marks
3.ENT Drugs and Pharmacology -100 marks
4.Opthalimic Drugs and Pharmacology-100 marks
5.Hormonal drugs -100 marks
Anatomy & Physiology of Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Anatomy and Physiology is an important subject for medical science. The study of Body Structure and its functions is Anatomy and Physiology. The systems of the Human Body are the Nervous System, Digestive System, Respiratory System, Cardiovascular System, Skeletal System, Muscular System, Endocrine System, Immune System, Lymphatic System, Covering System, and Urinary System.
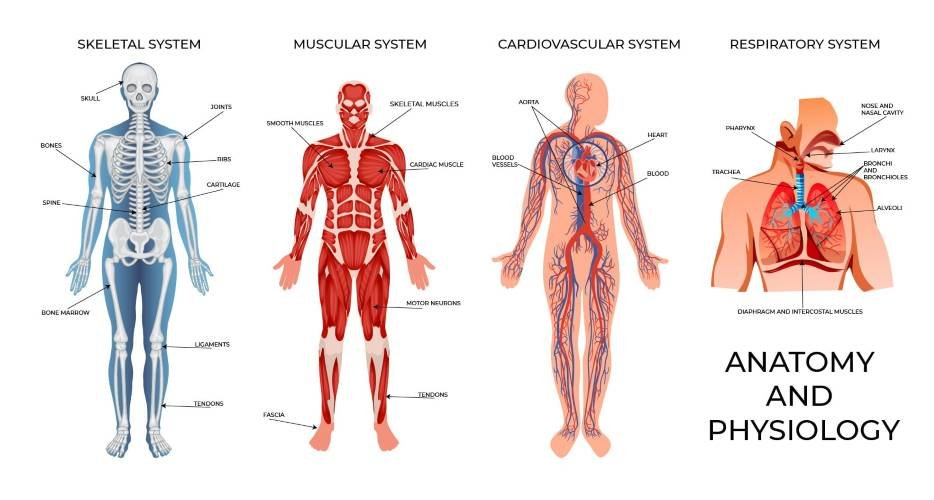
Anatomy and physiology (A&P) are the foundational sciences of the body: Anatomy studies the body’s structures and their physical relationships (the “what & where”), while Physiology studies how those structures function (the “how & why”). Together, they explain life, from atoms to organ systems, focusing on how the body maintains balance (homeostasis) through interconnected systems like cardiovascular, nervous, and respiratory. A key principle is the complementarity of structure and function: form dictates function, meaning the shape of a part enables its job, like heart chambers pumping blood
Anatomy: The Study of Structure Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
- Definition: The study of internal and external body structures and their relationships.
- Levels: From atoms and molecules to cells, tissues (muscle, nerve), organs (heart, liver), and organ systems (digestive, skeletal)
Physiology: The Study of Function Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
- Definition: The study of how the body’s parts work and support life.
- Focus: The chemical and physical processes, like cell respiration, nerve signals, and blood pumping.
Pharmacology of Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Pharmacology is the scientific study of drugs and their effects on living systems, including how they work, how the body responds, and their therapeutic and toxic effects. This field is a research-oriented biomedical science essential for discovering new medicines to fight diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and infections.
Pharmacology is broadly divided into two main areas
- Pharmacokinetics (PK): The study of what the body does to the drug. This involves the processes of absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME).
- Pharmacodynamics (PD): The study of what the drug does to the body. This involves the biological and physiological effects of drugs and their mechanisms of action, often at the molecular level, such as binding to specific receptors.
Key Principles of Pharmacology
- Mechanism of Action: How drugs interact with biological targets (like receptors or enzymes) at a molecular level to produce a response.
- Dose-Response: The relationship between the concentration of a drug and the magnitude of its effect.
- Therapeutic Index: The ratio between the dose that produces a desired (therapeutic) effect and the dose that produces a toxic effect, indicating the drug’s safety margin.
- Toxicity: The study of the adverse or harmful effects of chemicals and drugs
Pharmacology vs. Pharmacy
- Pharmacology is a research science focused on drug discovery and development, typically in a laboratory setting. Pharmacologists investigate how drugs work to identify new treatments and improve existing ones.
- Pharmacy is a patient-focused healthcare profession concerned with the preparation, dispensing, and proper use of medications in a clinical setting. Pharmacists work directly with patients and doctors to ensure safe and effective medication use
Study of OTC drug Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
The study of Over-the-Counter (OTC) drugs involves a multifaceted examination of non-prescription medications, their pharmacological properties, and the behavioral patterns of the consumers who use them for self-medication. As of 2025, modern healthcare research increasingly focuses on the balance between the convenience of these accessible medications and the significant public health risks associated with their misuse.
The following sections provide a detailed educational breakdown of the core components of OTC drug studies, ranging from regulatory definitions to global consumption trends and safety concerns.
1. Fundamental Definition and Regulatory Framework
OTC drugs, also known as non-prescription medications (NPMs), are pharmaceuticals that can be sold directly to consumers without a prescription from a healthcare professional.
- Regulatory Selection: In many countries, agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) select drugs for OTC status based on evidence that they are safe and effective when used without a doctor’s supervision.
- Approval Standards: For a drug to be classified as OTC, it must have a high therapeutic index, a large margin of safety, and a history of time-tested clinical usage.
- Rx-to-OTC Switches: Many modern OTC drugs, such as ibuprofen or loratadine, were originally prescription-only but were “switched” after long-term safety data proved they could be managed by laypeople.
2. Common Categories and Indications
Studies consistently identify several core classes of medications that dominate the global OTC market. These are typically used to treat “minor” or “self-limiting” conditions.
- Analgesics and Antipyretics: Pain relievers like acetaminophen (paracetamol), aspirin, and ibuprofen are the most frequently used OTC drugs globally.
- Gastrointestinal Aids: These include antacids (e.g., aluminum hydroxide), acid reducers (e.g., omeprazole), and anti-diarrheals (e.g., loperamide).
- Respiratory Remedies: Cough suppressants (e.g., dextromethorphan), decongestants (e.g., pseudoephedrine), and antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine).
- Nutritional Supplements: Vitamins and minerals are increasingly categorized alongside OTC drugs in consumer behavioral studies.
3. Consumer Behavior and Motivations
Research into self-medication practices (Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice or KAP studies) reveals several key drivers for choosing OTC options over professional consultations:
- Convenience and Time: Many users prefer OTC drugs to avoid time-consuming hospital visits.
- Cost-Effectiveness: OTC drugs are generally cheaper than the combined cost of a doctor’s consultation fee and prescription medication.
- Perceived Minor Illness: Patients often use their own judgment for what they perceive as non-serious ailments like headaches or colds.
- Independence: Adolescents, in particular, often use OTC drugs as a way to exercise independence in managing their health.
4. Critical Safety Risks and Misuse
Despite their “safe” classification, OTC drugs carry substantial risks, which are a major focus of recent 2025 clinical studies.
- Knowledge Gaps: A significant percentage of the population (often over 20-30% in studies) lacks knowledge regarding proper dosage or the potential for adverse reactions.
- Misclassification of Antibiotics: A widespread and dangerous trend in many regions (such as China and India) is the mistaken belief that antibiotics are OTC drugs, leading to inappropriate use and contributing to antimicrobial resistance.
- Potential for Abuse: Certain OTC drugs are frequently abused for non-medical reasons. For example, high doses of dextromethorphan (DXM) can cause hallucinations, and loperamide is sometimes misused for its opioid-like effects.
- Special Populations: OTC use in pregnant women, children, and the elderly requires extreme caution. For instance, aspirin is contraindicated for children recovering from viral infections due to the risk of Reye’s syndrome.
5. Economic and Public Health Impact
The study of OTC drugs also includes an analysis of their impact on the broader healthcare system.
- System Savings: OTC medications are estimated to save the U.S. healthcare system over $225 billion annually by reducing unnecessary physician visits and increasing workforce productivity.
- Pharmacist Role: Pharmacists are the critical human interface for OTC safety, often serving as the only professional filter to prevent dangerous drug-drug interactions.
- Digital Trends: The rise of online platforms for purchasing drugs has introduced new challenges, such as the lack of professional advice and the risk of counterfeit products.
Summary for Further Inquiry:
If you are conducting a specific study, you may want to focus on a particular demographic (e.g., adolescents or the elderly) or a specific geographical region, as local regulations and cultural attitudes significantly influence OTC medication patterns. Feel free to ask if you would like detailed data on a specific drug class or a particular country’s regulatory guidelines.
First Aid & Antimicrobial drugs for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
First Aid for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
In 2026, first aid remains the critical “bridge” of care between the moment an injury or illness occurs and the arrival of professional medical services. It is the immediate, often life-saving assistance provided to victims of accidents, sudden illnesses, or trauma. While it is not a substitute for professional medical treatment, mastering the basics of first aid empowers you to preserve life, prevent a patient’s condition from worsening, and promote a faster recovery.
Understanding first aid is as much about psychological preparedness as it is about physical technique. Staying calm under pressure allows you to assess a situation clearly, prioritize the most urgent needs, and provide reassurance to the casualty, which can significantly reduce their risk of shock. Whether you are dealing with a minor scrape at home or a critical cardiac event in public, the principles remain the same: safety first, swift assessment, and targeted action.
Antimicrobial drugs for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Antimicrobial drugs represent one of the most significant advancements in the history of medicine, fundamentally altering human life expectancy by providing a means to combat once-lethal infections. These medications are a broad category of agents—including antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, and antiparasitics—designed to kill or inhibit the growth of microorganisms. They function on the core principle of selective toxicity, meaning they are engineered to attack specific structures or metabolic pathways unique to microbes while leaving the human host’s cells relatively unharmed.
Core Classifications and Scope for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
The term “antimicrobial” is an umbrella that encompasses several specialized drug classes based on the type of organism they target:
- Antibacterial Drugs (Antibiotics): These target bacterial infections and are the most widely used. They are often subdivided into natural antibiotics (derived from molds or bacteria, like penicillin), semisynthetic (chemically modified for better efficacy), and synthetic agents (entirely man-made, like sulfonamides).
- Antiviral Drugs: These inhibit the development of viruses. Because viruses replicate inside human cells using the host’s machinery, designing these drugs is complex, as they must avoid damaging the human cell itself.
- Antifungal Agents: These are used to treat infections caused by fungi, such as yeasts and molds. Since fungi are eukaryotes (like humans), identifying unique targets that do not exist in the host is more difficult than with bacteria.
- Antiparasitic Drugs: These target parasites, ranging from microscopic protozoa (like those causing malaria) to multi-cellular helminths (worms).
Mechanisms of Action for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
Antimicrobial drugs work by disrupting essential life processes within the target microorganism. Major mechanisms include:
- Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis: Drugs like penicillins and cephalosporins prevent bacteria from building their rigid cell walls. Without this structure, the bacteria cannot withstand osmotic pressure and eventually burst (lysis).
- Inhibition of Protein Synthesis: Many drugs target the bacterial ribosome (which differs from the human version). By binding to these ribosomes, drugs like tetracyclines and macrolides stop the production of proteins essential for growth and survival.
- Inhibition of Nucleic Acid Synthesis: Some agents, such as fluoroquinolones, interfere with the enzymes responsible for DNA replication or RNA transcription, effectively preventing the microbe from reproducing.
- Disruption of Metabolic Pathways: Antimetabolites like sulfonamides act as “false ingredients” in essential biochemical pathways, such as the synthesis of folic acid, which bacteria must make themselves but humans obtain from food.
Clinical Considerations: Bactericidal vs. Bacteriostatic
A critical distinction in antimicrobial therapy is how the drug affects the pathogen:
- Bactericidal drugs actively kill the bacteria (e.g., penicillin).
- Bacteriostatic drugs merely inhibit growth, relying on the host’s immune system to eventually clear the stalled infection (e.g., tetracycline).
Pharmacology-2 for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
In 2026, Pharmacology-2 (often designated as Pharmacology II) stands as a pivotal advanced course in medical, pharmacy, and nursing curricula. This level of study transitions from the foundational “Pharmacology-1” concepts—like basic pharmacokinetics and general drug actions—to a sophisticated, system-oriented exploration of how medications treat complex diseases.
As of 2026, the global pharmaceutical landscape emphasizes not just how a drug works, but how it integrates with precision medicine, patient safety standards, and evolving clinical guidelines.
Core Systems Studied in Pharmacology-2 for Pharmacy Course in Dhaka
The curriculum for Pharmacology-2 is typically structured around major organ systems. Below are the primary domains covered in 2026 academic programs:
- Cardiovascular System (CVS) Pharmacology: This is frequently the largest module. It encompasses the management of hypertension, angina pectoris, cardiac arrhythmias, and congestive heart failure. Key drug classes include:
- Diuretics: Essential for managing fluid overload and blood pressure.
- Cardiac Glycosides: Specifically Digoxin, used for heart failure and atrial fibrillation.
- Anti-hypertensives: Including ACE inhibitors, Beta-blockers, and Calcium Channel Blockers.
- Drugs for Shock: Medications used to manage life-threatening conditions like hypovolemic or septic shock.
- Urinary System Pharmacology: Focuses on the kidneys and the regulation of fluid balance.
- Diuretics and Anti-diuretics: Mastery of these drugs is critical for treating edema and diabetes insipidus.
- Endocrine System Pharmacology: Investigates the complex world of hormonal therapies.
- Diabetes Management: In 2026, this includes advanced insulin analogues and oral hypoglycemic agents.
- Thyroid and Pituitary Hormones: Drugs used to correct glandular imbalances.
- Reproductive Health: Including oral contraceptives, androgens, and estrogens.
- Autacoids and Related Drugs: This includes the study of local hormones and inflammation mediators.
- Histamines and NSAIDs: Essential for treating allergies, pain, and inflammatory conditions like gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
 MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka
MATCDHAKA – Medical Assistant Training Centre in Dhaka Pharmacy, Veterinary, Dental, Nursing, Pathology, Physiotherapy and Homeopathy Training Institute in Dhaka